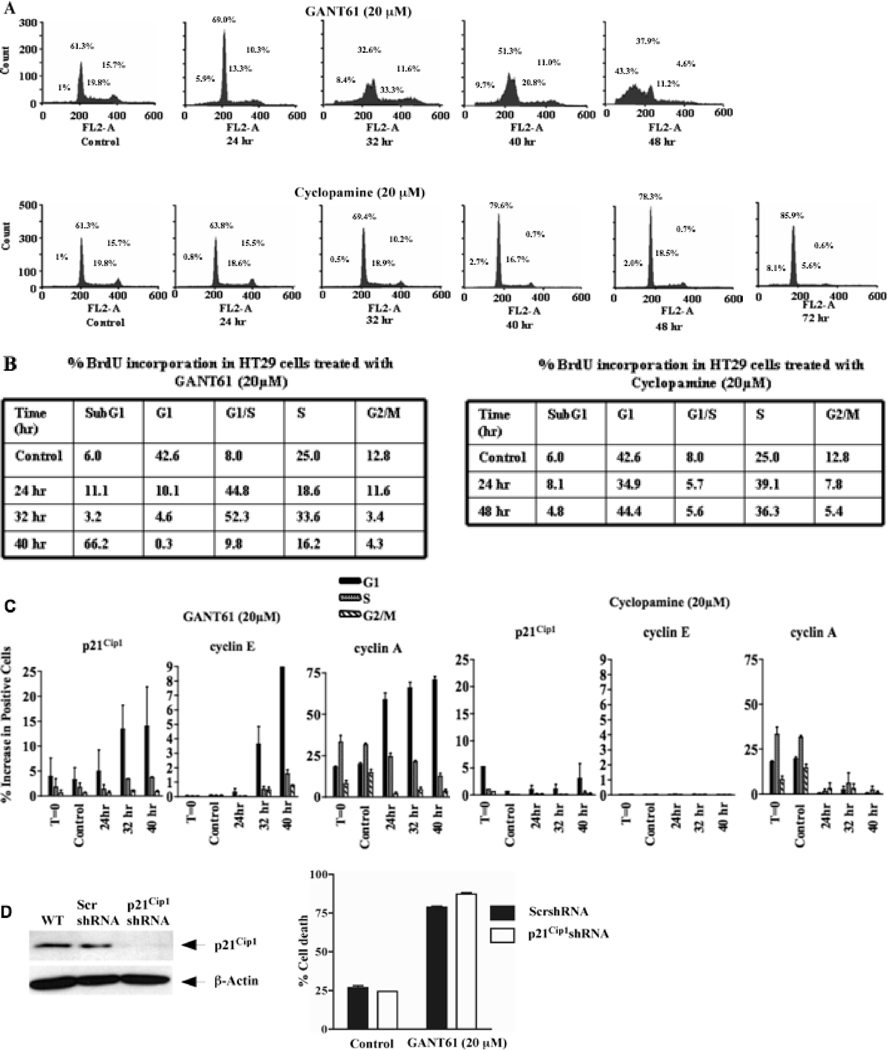
Figure 1.
GANT61 induces accumulation of HT29 cells at G1/S and early S in contrast to cyclopamine. HT29 cells were treated with A: GANT61 (20 µM) or cyclopamine (20 µM) for up to 72 hr. DNA was extracted, stained and cell cycle distribution was analyzed using flow cytometry. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. B: BrdU incorporation demonstrates accumulation of GANT61-treated cells at the G1/S boundary and in early S. HT29 cells were treated with GANT61 (20 µM) or cyclopamine (20 µM) for up to 48 hr. % BrdU incorporation was determined using flow cytometry. Data are representative of duplicate determinations. C. Bivariate flow cytometric analysis of p21Cip1, cyclin E and cyclin A expression in different phases of the cell cycle. HT29 cells were treated with GANT61 (20 µM) or cyclopamine (20 µM) for up to 40 hr, followed by staining and cell cycle analysis. Data are representative of duplicate determinations. D: Influence of stable p21Cip1shRNA knockdown on sensitivity of HT29 cells to GANT61. HT29 cells stably expressing p21Cip1- or scrambled-shRNA were treated for 72 hr with GANT61 (20 µM). Cell death was analyzed by Annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry. Data represent the mean ± SD of duplicate determinations. Reduced expression of p21Cip1 was confirmed by western analysis.