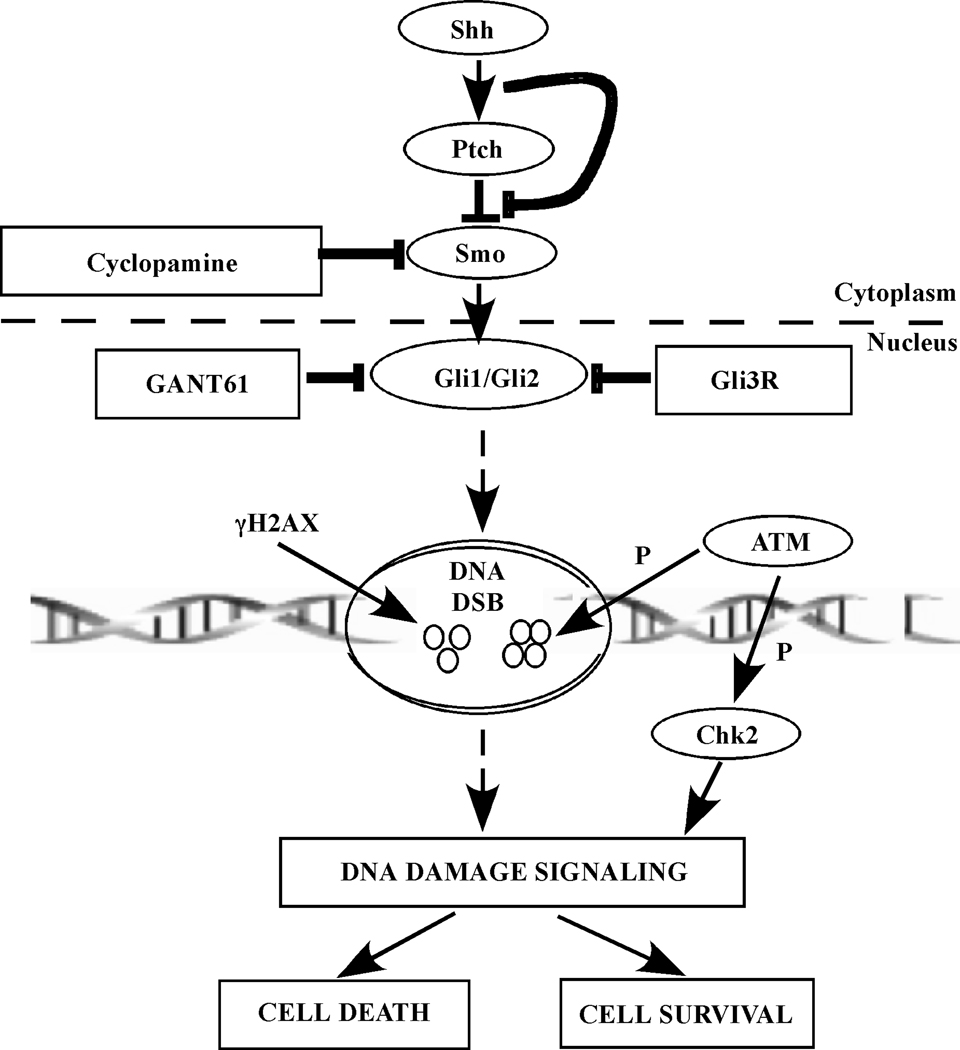
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of the mechanisms underlying inhibition of HH/Gli signaling that result in cell death. Targeting Smo by cyclopamine is upstream and less effective than targeting Gli1/Gli2 by either GANT61 or Gli3R in eliciting cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Blocking Gli1/Gli2 function with GANT61 or Gli3R induces DNA damage marked by formation of γH2AX foci at DNA break sites. An ATM/Chk2 axis is involved in DNA damage signaling downstream of inhibiting Gli1/Gli2 activity. P represents phosphorylation and DSB is double strand break.