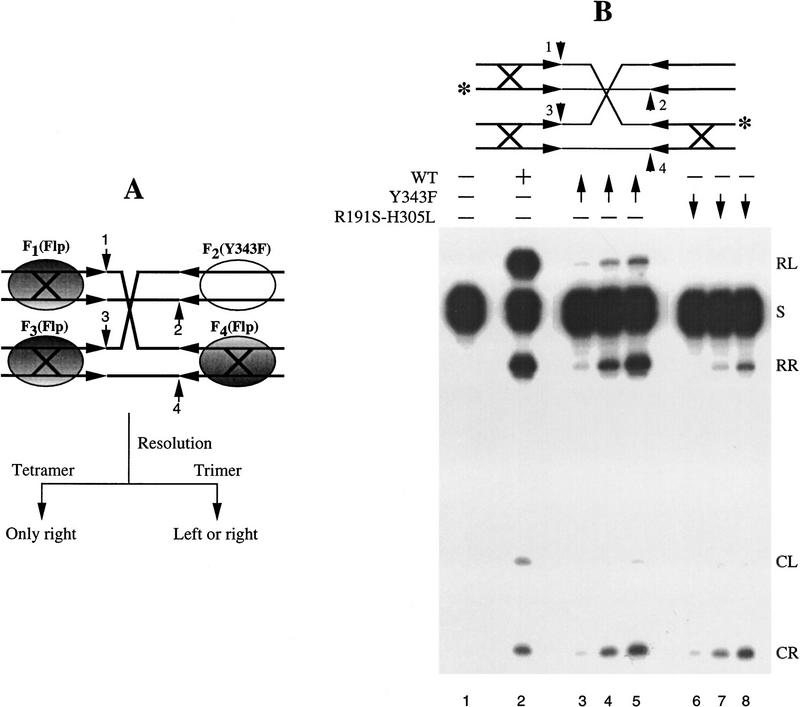
Figure 5.
Verification of the anticipated resolution events from the trimer and dimeric dimer models for a given arrangement of the three to one Flp to Flp(Y343F) tetramer. (A) The normal Flp-binding element in the Holliday junction had the sequence 5′-GAAGTTCCTATTC-3′/3′-CTTCAAGGATAAG-5′. In the weakened arms (large X), the CG pair at position 7 was replaced by an AT pair (Lee et al. 1996). The junction contained the native spacer sequence 5′-TTTCTAGA-3′/3′-AAAGATCT-5′. By means of a directed protein replacement strategy described earlier (Lee et al. 1994), one Flp(Y343F) monomer and three wild-type Flp monomers can be placed on the one normal Flp-binding arm and the three weakened arms, respectively. If a trimer within the tetramer is the active species, resolution of the junction at the left end of the spacer can occur by the action of the F1–F3–F4 trimer set. Similarly, resolution at the right end can occur by the action of the F2–F3–F4 trimer set. In this case, the reaction derives the two triad domains from F2 [Flp(Y343F)] and F4, and the two Tyr-343 residues from F3 and F4, respectively. The Tyr-343 is not essential for the strand joining reaction. Thus, the trimer model predicts equivalent resolutions at the left and right ends. If the tetramer (dimeric dimer) is the active species, resolution can only occur at the right. Left resolution is ruled out because Flp(Y343F) (F2) bound to the normal arm cannot provide the cleavage nucleophile. (B) Holliday junction was labeled at the 3′ end (asterisk) on two strands so as to monitor resolution at the left or the right end of the spacer. The short vertical arrows numbered 1–4 indicate the points of strand cleavage by Flp. In targeted protein placement experiments, the initial binding was done with Flp(Y343F) at ∼8–10 monomers per binding arm. The high molar ratio of protein to DNA ensured that virtually all of the normal arms in the substrate population were stably occupied by this protein. After 10-min preincubation at 30°C, an 8–10 molar excess [over Flp(Y343F)] of Flp (lanes 3–5) or Flp(R191S, H305L) (lanes 6–8) was added to the reaction mixture. Samples were analyzed at 10 min following the addition of the second protein. Lane 1 is a control reaction to which neither Flp nor a Flp variant was added. Lane 2 represents a 10 min reaction with wild-type Flp (∼8–10 protein monomers per binding arm) in 200 mm NaCl. The final NaCl concentrations were 100 mm in lanes 3 and 6, 150 mm in lanes 4 and 7, and 200 mm in lanes 5 and 8. The NaCl concentration prior to the addition of the second protein was 20 mm less in each case. The product bands corresponding to resolution at the left end (1,3 resolution) and the right end (2,4 resolution) are named RL and RR, respectively. CR is the radioactive cleavage band from the right (cleavage at 2); CL is from the left (cleavage at 1).