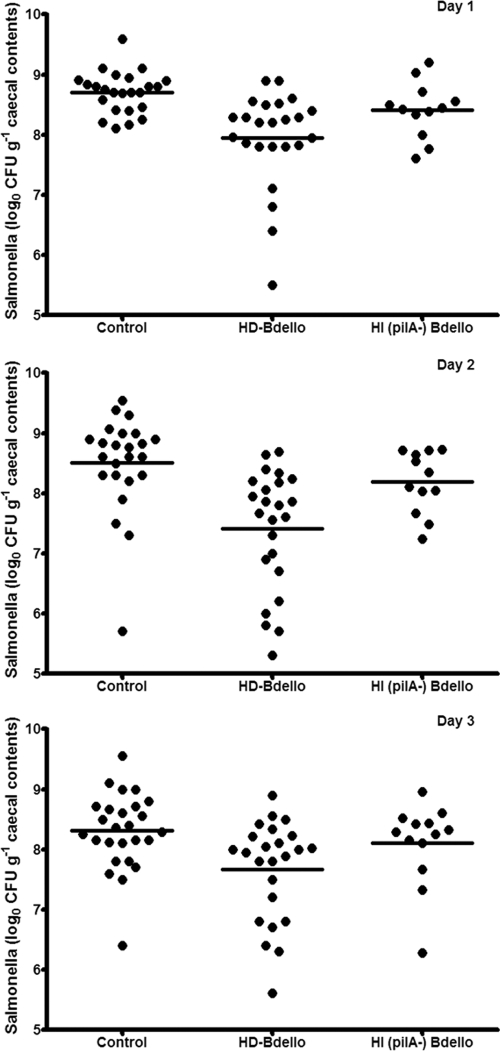
Fig. 3.
Scatter plot showing the effect of Bdellovibrio treatment on colonization of chicken ceca by Salmonella Enteritidis. Ten groups of 18 Hy-line brown chicks each were challenged orally with approximately 3 × 107 CFU of S. Enteritidis P125109 at 2 days of age. Four of these groups subsequently were dosed orally with approximately 9.8 × 107 PFU of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus HD100 at 6 days of age. Two further groups were dosed with nonpredatory HI ΔpilA Bdellovibrio, matched to the predatory Bdellovibrio number by total protein content. During each of the 3 days following Bdellovibrio treatment, six birds from each group were sacrificed, and the number of Salmonella organisms in the cecal contents of each bird was determined by spread-plating serial dilutions of cecal suspensions onto brilliant green agar. The results from four independent biological repeats were pooled from each day. Each data point represents the number of Salmonella organisms in the cecal contents of a single bird. The horizontal line represents the means for each group.