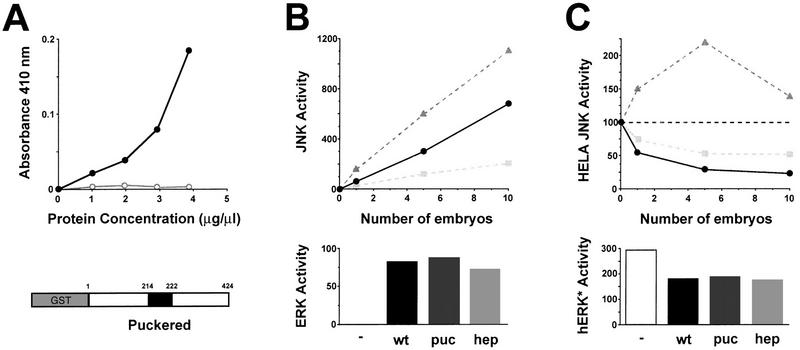
Figure 3.
puc encodes a JNK phosphatase. (A) In vitro phosphatase activity of a GST–Puc fusion protein. Results of PNPP assay in which cleavage of PNPP was measured by change in absorbance at 410 nm as a function of added protein. (•) Purified GST–Puc protein; (○) control points from extracts obtained from untransformed bacteria following similar protocols. (Bottom) Schematic representation of the fusion protein. The phosphatase catalytic domain is highlighted in black (residues 214–222). (B) Endogenous JNK and ERK activity of wild-type (wt), pucE69/pucE69 (puc) and hep1/hep1 (hep) embryos. (Top) JNK assays were performed with normalized amounts of embryo extracts (1 embryo/μl) prepared in the presence of phosphatase inhibitors (as indicated in Materials and Methods). Kinase activity is measured in arbitrary units from imaging analysis. (Solid circles) Wild-type (wt) extracts; (shaded triangles) puc embryo extracts; (shaded squares) hep embryos. JNK activity increases twofold in puc mutants and reduced threefold in hep. (Bottom) ERK assays were performed by in-gel kinase assay with a normalized amount of extract, in the linear range for JNK, equivalent to five embryos. Histograms represent quantitation of kinase activity (arbitrary units). Wild-type, puc, and hep extracts have equivalent levels of ERK activity. (C) Puc phosphatase activity on heterologous JNK and ERK. (Top) JNK activity induced in HeLa cells was measured in the absence of any extract to deduce the basal level of activity (100% JNK activity—broken line). Equivalent amounts were incubated with normalized embryo extracts (1 embryo/μl) prepared in the absence of phosphatase inhibitors. The results are expressed in percentage of JNK activity. (Solid circles) Wild-type extracts; (shaded triangles) puc embryo extracts; (shaded squares) hep embryos. Wild-type embryos have high levels of JNK phosphatase activity (HeLa JNK activity is reduced fivefold). Puc extracts do not show JNK phosphatase activity, indeed HeLa JNK activity gets increased because of the high levels of JNK activity of puc extracts (it can be brought back to basal levels by previous heat inactivation; see also Discussion). In hep extracts, JNK phosphatase activity is reduced to 50% of that of wild-type embryos. (Bottom) ERK activity of preactivated human ERK (hERK*) was assayed as indicated in Materials and Methods. Extracts (5 embryos) from wild-type, puc, and hep embryos display the same level of ERK phosphatase activity, reducing hERK* activity by 40%. Histograms represent quantitation of kinase activity (arbitrary units). Positive controls were performed with purified CL100 phosphatase (50 μg/ml) (data not shown).