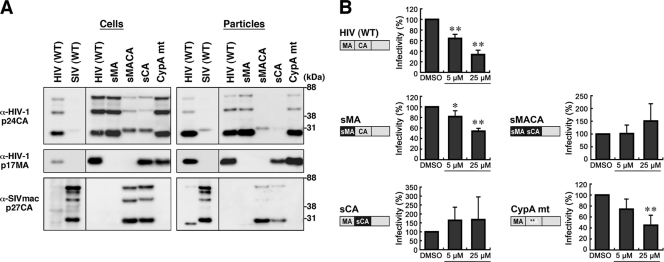
Fig. 6.
Mapping of Gag domain responsible for inhibition. (A) Intracellular Gag expression and particle production. 293FT cells were cotransfected with pHIVgag-pol expressing chimeric Gag, pLenti-luciferase, pRevpac, and a plasmid expressing VSV-G, and virus particles produced were purified by ultracentrifugation. Cells and particles were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-HIV-1 p24CA and p17MA and anti-SIVmac p27CA antibodies. (B) Single-round infection assays with the Gag domain chimeras and Gag mutants with amino acid substitutions. The corresponding domain of SIVmac Gag (black) was introduced into HIV-1 Gag background (gray), and the resultant chimera was referred to as “s” plus the name of the corresponding domain of SIVmac. WT, wild type; sMA, HIV containing replacement of MA with SIV MA; sMACA, HIV containing replacement of MACA with SIV MACA; sCA, HIV containing replacement of CA with SIV CA. CypA mt represents HIV with amino acid substitutions G89A and P90A in the CypA-binding loop of CA NTD (denoted by asterisks). Following infection, the cell culture was incubated in the presence of 5 and 25 μM BMMP. Viral infectivity was monitored by luciferase reporter assays. Data were shown as means with standard deviations from 4 to 6 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.