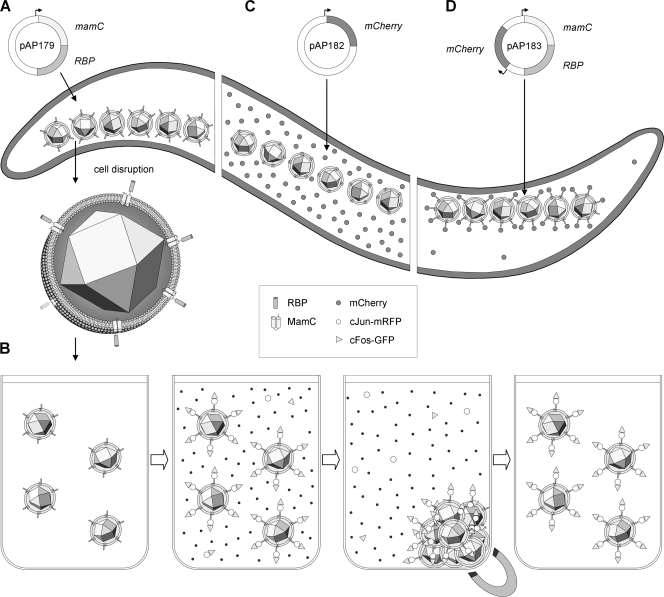
Fig. 1.
Schematic overview of the approach for MamC-RBP and RFP/mCherry expression in M. gryphiswaldense and the application of modified magnetosomes for immunoprecipitation. (A) Transformation of bacteria with pAP179 resulted in expression and magnetosome targeting of MamC-RBP fusion protein due to MamC serving as an MM anchor. (B) Application of MamC-RBP-decorated magnetosomes for coimmunoprecipitation (IP). The modified magnetosomes were isolated from disrupted cells, equilibrated in IP buffer, and incubated with RFP-tagged c-Jun protein. Interacting c-Fos-GFP protein was pulled down after incubation with cell lysate (Co-IP). The bound proteins were separated magnetically or by centrifugation, whereas residual noninteracting proteins were removed by washing. (C) mCherry alone is expressed from pAP182 and disperses in the cytoplasm in the absence of MamC-RBP. (D) Coexpression of MamC-RBP and mCherry from pAP183 results in efficient recruitment of the soluble mCherry protein to the magnetosomes expressing MamC-RBP and its depletion from cytoplasm.