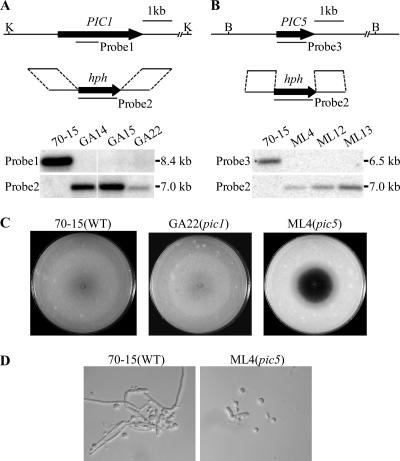
Fig. 2.
Targeted deletion of the PIC1 and PIC5 genes. (A) Schematic diagram of the PIC1 gene and gene replacement construct and Southern blots of KpnI-digested genomic DNA of the wild type (70-15) and pic1 mutants (GA14, GA15, and GA22) hybridized with probe 1 and probe 2. (B) Schematic diagram of the PIC5 gene replacement constuct and Southern blots of BamHI-digested DNA of 70-15 and pic5 mutants (ML4, ML12, and ML13) hybridized with probe 2 and probe 3. (C) Oatmeal agar cultures of 70-15, GA22, and ML4. Photographs were taken after incubation for 10 days. The central part of the ML4 colony underwent autolysis and became darkly pigmented. (D) Hyphae harvested from 2-day-old CM cultures of 70-15 and mutant ML4 were digested with 5 mg/ml lytic enzyme for 40 min. The pic5 mutant produced abundant spheroplasts and had almost no hyphal fragments left.