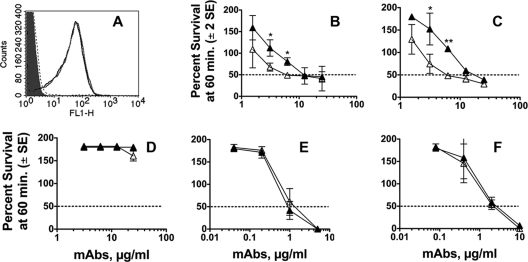
Fig. 5.
Bactericidal activities of anti-fHbp MAbs measured against a mutant of group B H44/76 with genetic inactivation of NspA expression. (A) Binding of purified human fH (100 μg/ml) to live bacteria determined by flow cytometry. Gray line, NspA KO mutant; black line, wild-type control; dashed line, double fHbp and NspA KO control; light gray filled area, no fH. All three strains showed similar binding with a control anti-PorA P1.7 MAb (data not shown). (B to F) Survival of bacteria after incubation for 60 min at 37°C with each of the MAbs and 20% IgG-depleted human serum as a complement source. Open triangles, NspA KO mutant; closed triangles, control wild-type strain. (B) Chimeric anti-fHbp MAb JAR 3. (C) Chimeric anti-fHbp MAb JAR 5. (D) Chimeric anti-fHbp MAb502. (E) Control murine anti-PorA P1.7 MAb. (F) Control murine MAb, SEAM 12 reactive with group B capsule. Bactericidal activity results are from three independent experiments. Where indicated, survivals of the respective wild-type and NspA KO strains incubated at the MAb dilution were significantly different (*, P ≤ 0.02; **, P < 0.001).