Fig. 10.
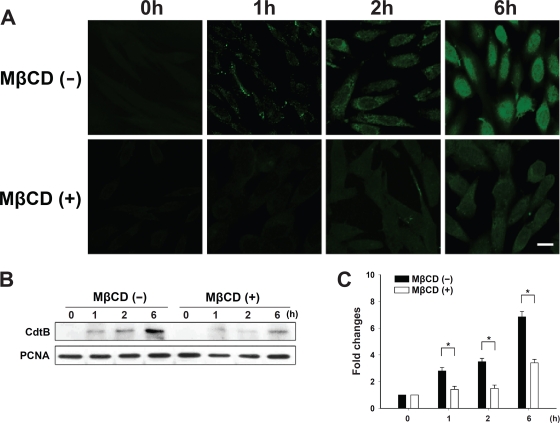
Depletion of cholesterol prevents the nuclear localization of C. jejuni CdtB. (A) CHO-K1 cells were untreated or treated with 10 mM MβCD for 1 h prior to exposure to 200 nM CDT holotoxin at 37°C for the indicated times. The cells were washed and probed with anti-CdtB antiserum, followed by staining with FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. The stained cells then were analyzed by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) The nuclear fraction from cell lysates was prepared from CHO-K1 cells untreated or treated with 10 mM MβCD for 1 h, followed by incubation at 37°C in the presence of CDT holotoxin for the indicated times. CdtB in the nucleus of cell lysates was detected by Western blotting. The results represent three independent experiments. PCNA was used as a loading control for the nuclear fraction of cell lysates. (C) Protein expression levels were analyzed using scanning densitometry. The lower right panel shows the quantitative data for the nuclear CdtB signal. An asterisk indicates P < 0.05 compared to results for each untreated MβCD group, as determined by Student's t test. MβCD, methyl-β-cyclodextrin; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen.