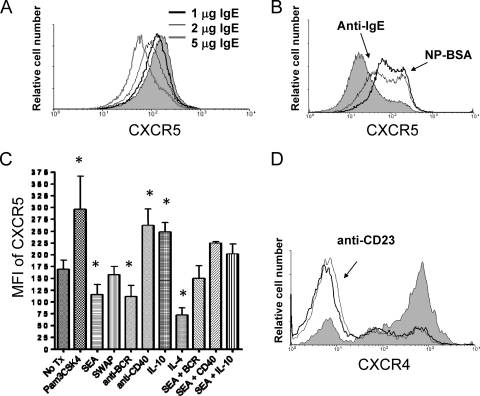
Fig. 4.
CD23-bound IgE cross-linking increases CXCR5 but reduces CXCR4 expression. (A) Increasing levels of exogenous IgE reduce surface levels of CXCR5 on IL-4-treated tonsil B cells. B cells were incubated for 18 h and evaluated by flow cytometry. Gray fill, untreated B cells. Results are representative of 3 experiments with 3 tonsils. (B) CD23-bound IgE cross-linking increases surface levels of CXCR5. NP-specific IgE was cross-linked by NP-BSA (thick black line) or anti-IgE (thin black line). Gray fill, untreated B cells. NP-BSA in the absence of IgE or an isotype control did not affect CXCR5 levels (not shown). Results are representative of 4 experiments with 4 tonsils. (C) Effect of B cell stimuli on CXCR5 levels. Tonsil B cells were treated with the indicated stimuli for 18 h, and CXCR5 levels were assessed by flow cytometry. Pam3CSK4 (TLR2 ligand), anti-CD40, and IL-10 increased levels of CXCR5, whereas SEA, anti-BCR, and IL-4 reduced levels. SWAP had no effect on CXCR5 surface levels (4 tonsils; *, P < 0.05 compared to untreated [No Tx] B cells). (D) CD23 cross-linking reduces CXCR4 expression on Ramos B cells. Gray line, 1 μg/ml anti-CD23; thick black line, 5 μg/ml anti-CD23; gray fill, untreated cells. Results are representative of 6 separate experiments. Similar results were obtained with tonsil B cells.