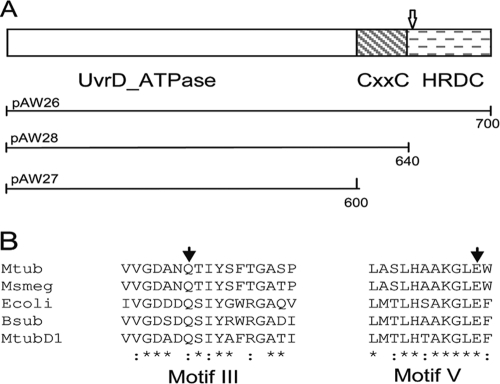
Fig. 2.
Domain structure and sequence alignment of UvrD2. (A) Domain structure of M. tuberculosisUvrD2, showing the N-terminal UvrD ATPase domain and the C-terminal HRDC domain separated by the tetracysteine motif-containing domain. The position of the transposon insertion identified in M. tuberculosisCDC1551 is indicated with an arrow. The extents of the full-length and truncated constructs used in the complement switch experiments are shown below the structure, with the numbers indicating the numbers of amino acid residues. (B) Partial alignment of UvrD2 sequences from M. tuberculosis(Mtub) and M. smegmatis(Msmeg) with those of UvrD homologues from E. coli(Ecoli) and Bacillus subtilis(Bsub) and of UvrD1 from M. tuberculosis(MtubD1). The sequences shown are for motif III and motif V of the ATPase domain, with the conserved residues mutated in this study indicated by filled arrowheads.