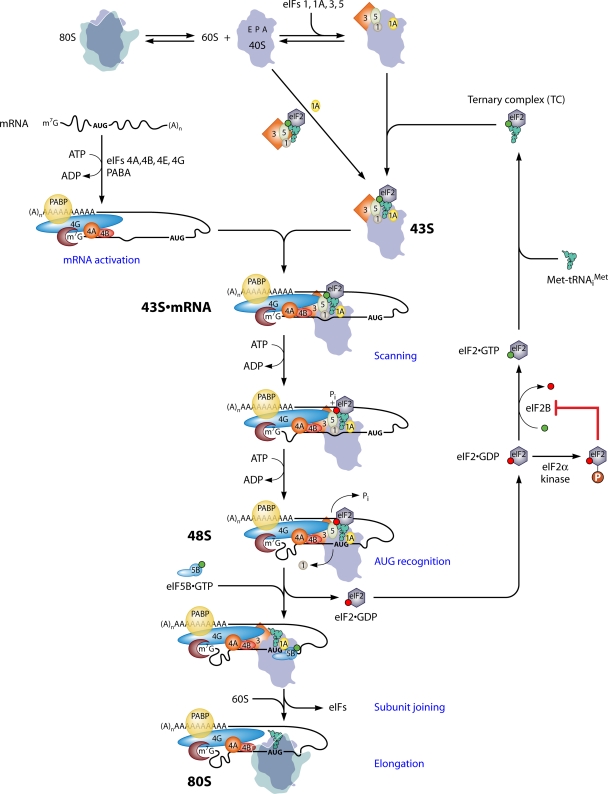
Fig. 1.
Pathway of eukaryotic translation initiation via ribosomal scanning. The process of initiation is depicted as a pathway of reactions (a subset described in blue type), beginning with the dissociation of 80S ribosomes into free 40S and 60S subunits and the assembly of the 43S PIC on the small ribosomal subunit. 80S ribosomes and 40S subunits are depicted as silhouettes of the crystal structures of bacterial 70S and 30S ribosomal species, with approximate locations of the aminoacyl-tRNA (A), peptidyl-tRNA (P), and exit (E) sites labeled in the 40S subunit. eIFs are depicted as shapes labeled by numbers, and GTP or GDP bound to eIF2 in the ternary complex (TC) is depicted as green or red balls, respectively. Two pathways for the recruitment of the TC to the 40S subunit in assembling the 43S PIC are depicted, with one involving the prior incorporation of the TC into the multifactor complex (MFC). mRNA is activated by the binding of eIF4F (eIF4E/eIF4G/eIF4A) to the m7G cap and of PABP to the poly(A) tail of the mRNA, with the attendant production of a single-stranded region at the mRNA 5′ end in a manner facilitated by eIF4B and the ATP-dependent helicase activity of eIF4A. 43S PICs attach to the 5′ end of the mRNA, forming the 43S·mRNA complex, in a manner stabilized by a network of interactions among the mRNA, eIF4G, eIF3, eIF5, eIF4B, and the 40S subunit. The 43S PIC scans the mRNA 5′UTR in a manner facilitated by eIF4A's helicase activity, and the helicases Ded1 and Dhx29 (not shown) also facilitate scanning through stable secondary structures in the 5′UTR. Note that the hydrolysis of the GTP in the TC occurs in the scanning complex, but the release of Pi is blocked until the AUG base pairs with the anticodon of Met-tRNAiMet, with the attendant dissociation of eIF1 from the 40S subunit and the arrest of scanning. eIF2-GDP is released from Met-tRNAiMet, and eIF5B-GTP joins the complex to catalyze the joining of the 60S subunit and the production of an 80S initiation complex competent for elongation. The eIF2-GDP is recycled to the eIF2-GTP by the GEF eIF2B to enable the reassembly of the TC. eIF2B is inhibited by the phosphorylation of eIF2 on Ser-51 of its α subunit by various kinases, activated by different kinds of stress. See the text for more details. (Modified from reference 85 with permission of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.)