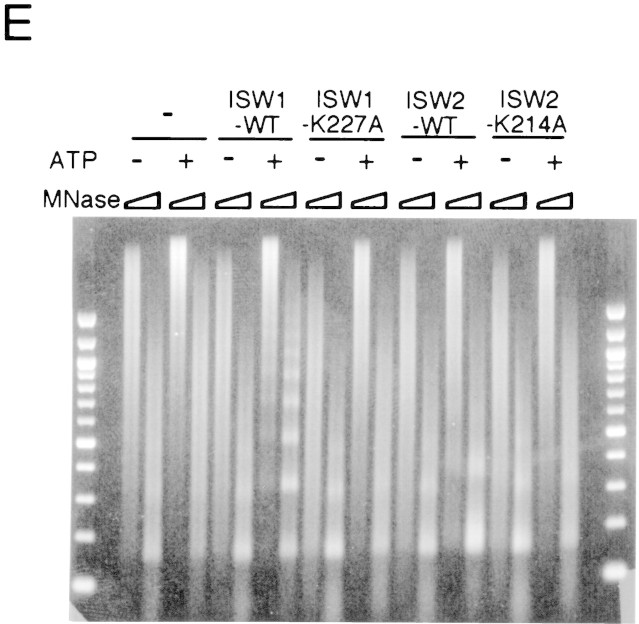
Figure 5.
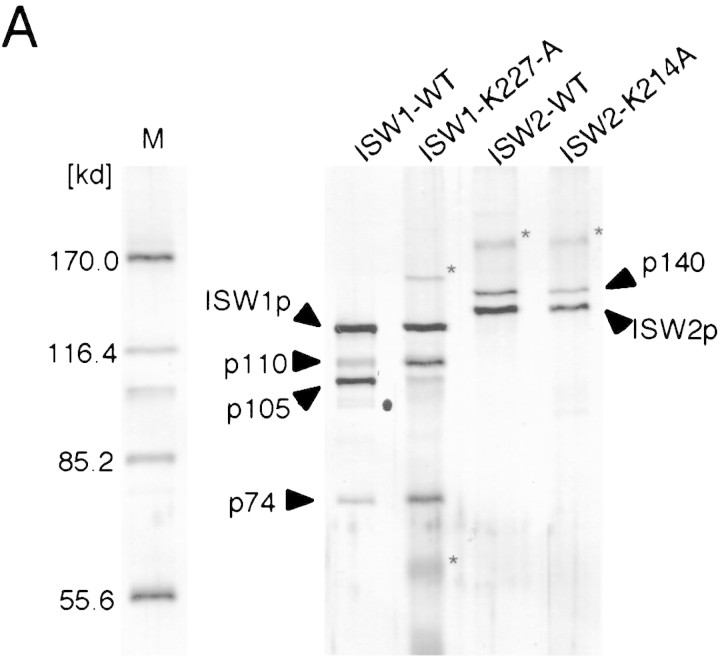
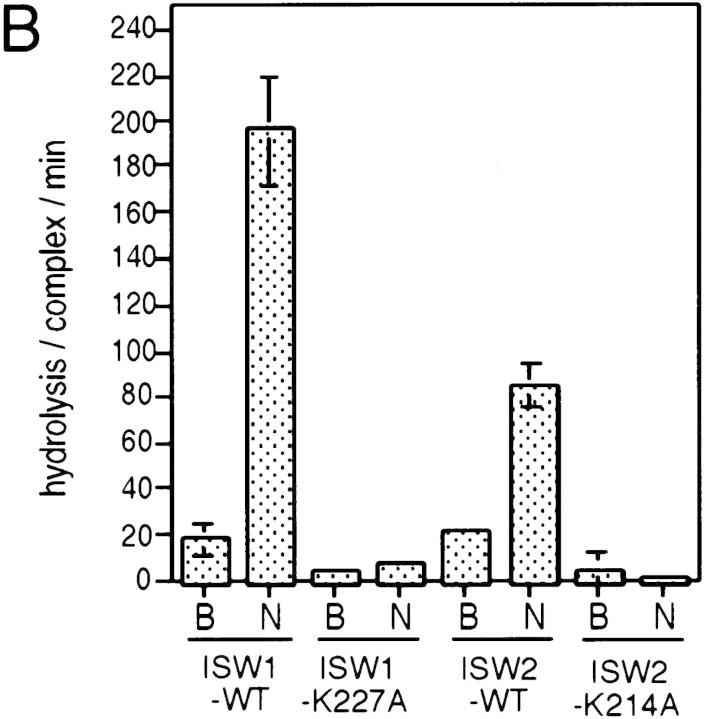
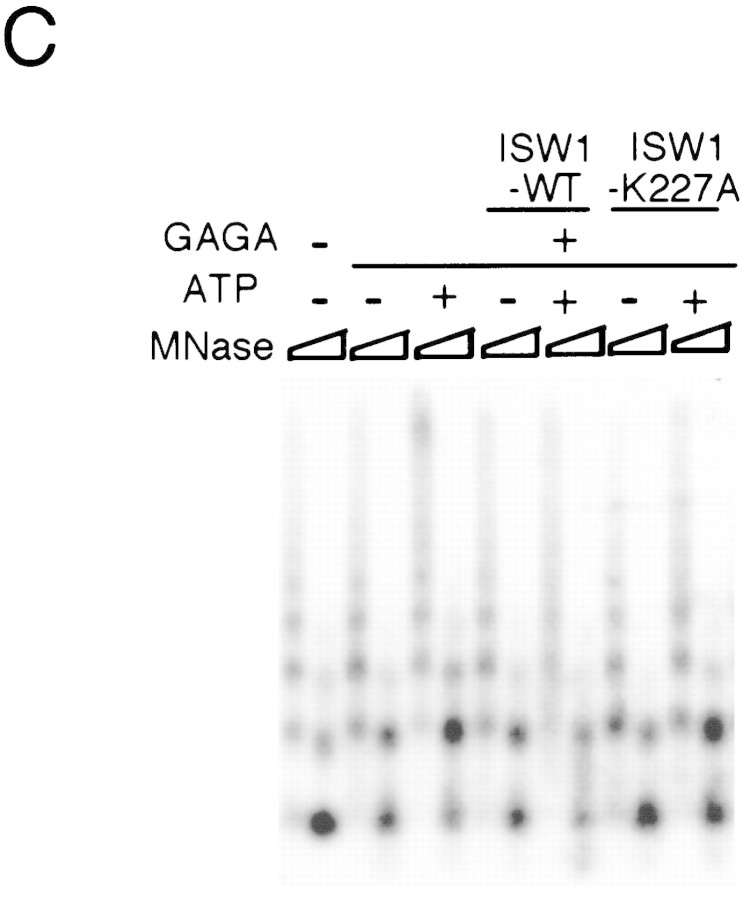
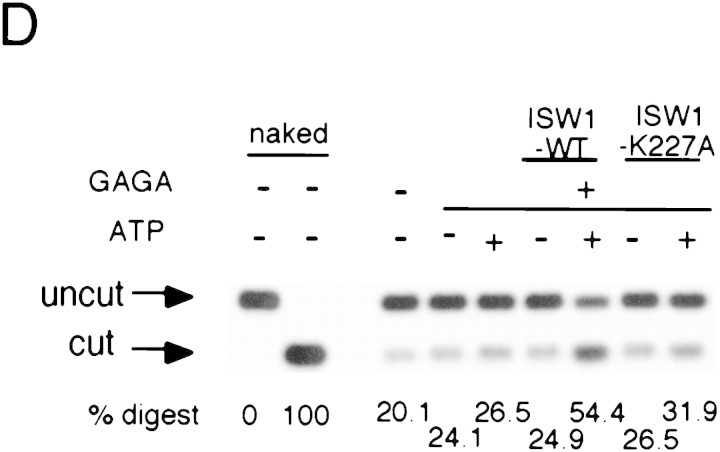
A single amino acid substitution within the ATPase domain of both yeast ISWI proteins inactivates ATP-dependent activities of the yeast ISWI complexes. (A) Subunit composition of the mutant yeast ISWI complexes. Purified wild-type and mutant yeast ISWI complexes were separated on an 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and stained by silver. (Arrows) The subunits of the complexes. (●) Proteolytic products; (*) contaminants. (B) Mutant yeast ISWI complexes are defective in the ATPase activities. The ATPase assays were done in buffer (B) or in the presence of nucleosomes (N). Hydrolysis/complex per min denotes the molecules of ATP hydrolyzed by one molecule of the ISWI complex/min. Bars and vertical lines represent the average and the standard deviation, respectively, calculated from three independent experiments. (C–E) The mutant yeast ISWI complexes are defective in the MNase ladder assay, restriction enzyme accessibility assay, and nucleosome spacing assay, respectively. All assays were done in the standard conditions. For C and E, partial and extended MNase digestions were performed for each sample.