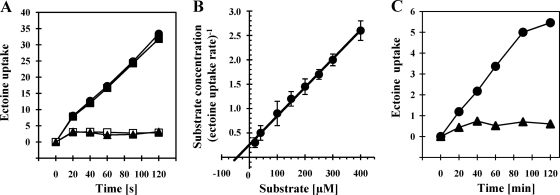
Fig. 2.
Uptake of radiolabeled [14C]ectoine under salt and cold stress conditions. (A) V. pantothenticus cells were grown in SMM (open squares), SMM with 0.4 M NaCl (closed squares), 0.67 M sucrose (closed circles), or 0.68 M glycerol (closed triangles) to early exponential growth phase (OD578 of about 0.4). The cells then were assayed for [14C]ectoine uptake in the respective growth medium at a final substrate concentration of 14 μM; [14C]ectoine uptake by the cells is given in nmol ectoine (mg protein)−1. The data shown are from representative transport experiments selected from three independent biological replicas. (B) [14C]ectoine uptake rates were determined in salt-shocked (with 0.7 M NaCl) cultures (60 min after the cold shock) at the indicated substrate concentrations of ectoine. The measured [14C]ectoine rates were plotted as substrate concentration (μM) per transport rate [nmol ectoine (mg protein min)−1] versus the substrate concentration (μM) according to Hanes-Woolf. The data shown represent three independent sets of experiments with errors given as standard deviations. (C) V. pantothenticus cells were grown in SMM either at 37°C (triangles) or at 15°C (circles) to early exponential growth phase (OD578 of about 0.4). The cells then were assayed in SMM for [14C]ectoine uptake at a final substrate concentration of 14 μM; [14C]ectoine uptake is given as nmol ectoine (mg protein)−1. The data shown are representative transport experiments selected from three biological replicas.