Figure 1.
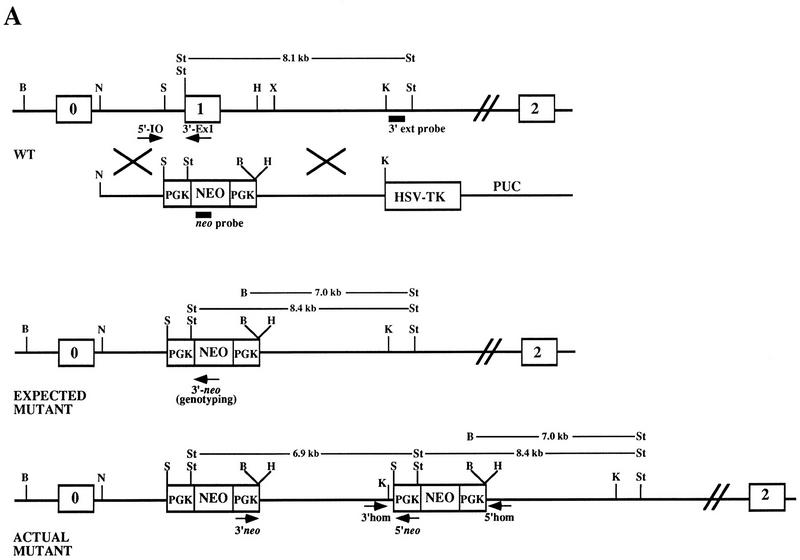
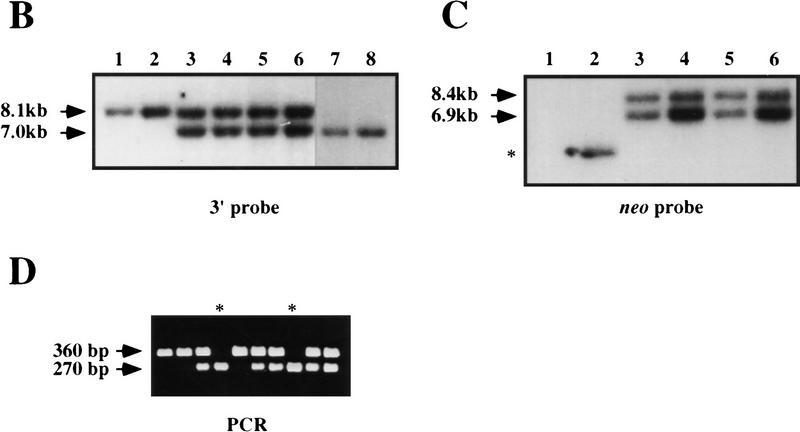
Disruption of K-ras in ES cells. (A) The K-ras targeting vector pK-ras KO was constructed by inserting fragments from intron 0 and intron 1 of the mouse K-ras gene into the plasmid pPNT. The regions of homology consist of a 2.8-kb NotI–SalI fragment and a 5.1-kb HindIII–KpnI fragment. Both the pkg-neo and HSV-tk cassettes were positioned such that they were transcribed in the same transcriptional orientation as K-ras. (B) Southern blot analysis of BamHI plus StuI-digested genomic DNA from ES cell clones using a probe 3′ to the region of homology (3′ ext probe). Lanes 3–6 represent four independent K-ras+/− ES cells clones, as they possess both an 8.1-kb wild-type (wt) allele and a 7.0-kb mutant-specific K-ras allele. (Lane 1) The DNA is from wild-type ES cells; (lane 2) from a nonhomologous integrant; and (lanes 7,8) two independent K-ras−/− mutant ES cell clones that were obtained after exposure to increasing concentrations of G418. (C) Southern blot analysis of StuI-digested genomic DNA using a probe specific for neo. On a parallel set of samples to C the neo probe detected the expected 8.4-kb StuI fragment, as well as an additional 6.9-kb fragment in all K-ras+/− ES cell clones (lanes 3–6). As expected, no signal was detected in the wild-type ES cells (lane 1), and the lower band depicted in lane 2 represents the random integration pattern for this nonhomologous integrant. A number of different digests were performed and screened with the above probes, as well as with probes 5′ to the region of homology, within the 5′ region of homology, and spanning the PGK promoter sequence to determine the actual configuration of the mutant allele. Both the expected and actual K-ras mutant allele configurations are shown in A. This was confirmed further by PCR analysis using the primer pairs shown in A. Primer pairs 3′ neo + 5′ neo and 3′ homolog + 5′ homolog specifically amplify a 5.1- and a 1.8-kb fragment, respectively, as would be expected for this configuration. This head-to-tail integration pattern occurred either one time (lanes 3,5) or multiple times (B lanes 4,6). (D) PCR analysis of E12.5 embryos derived from a K-ras+/− intercross showing the presence of K-ras−/− embryos (lanes marked with an asterisk). The two alleles can be distinguished using primer pairs that specifically amplify a 360-bp wild-type fragment (5′ I0 + 3′ Ex1) or a 270-bp mutant specific fragment (5′ I0 + 3′ neo).