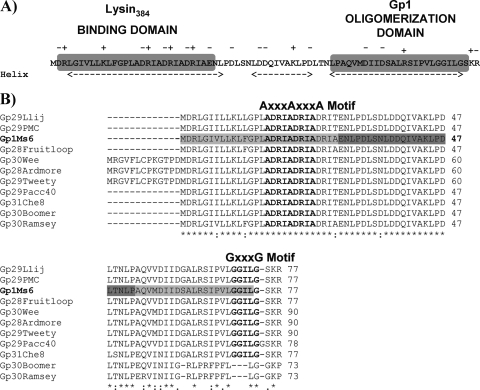
Fig. 2.
(A) Gp1 secondary structure protein prediction according to the Chou and Fasman algorithm (4, 5; http://www.biogem.org/tool/chou-fasman/). Charged residues in the Gp1 amino acid sequence are indicated by + or −. N-terminal lysin384-binding and C-terminal homo-oligomerization domains on Gp1 are indicated in gray boxes. (B) CLUSTALW alignment of Ms6 Gp1 (AAG48317) with similar sequences of members included in subcluster F1, namely, Llij Gp29 (ABD58248), PMC Gp29 (ABE67530), Fruitloop Gp28 (YP002241713), Wee Gp30 (YP004123852), Ardmore Gp28 (ACY39910), Tweety Gp29 (YP001469262), Pacc40 Gp29 (YP002241613), Che8 Gp31 (NP817369), Boomer Gp30 (YP002014246), and Ramsey Gp30 (YP002241817) (the primary accession numbers in the UniProtKB/TrEmb1 database are given in parentheses). Identical (*), highly similar (:), and similar (·) amino acids are indicated. Numbers refer to the amino acids positions. The AXXXAXXXA and GXXXG motifs are indicated in bold above the protein amino acid sequence. N-terminal/C-terminal and central Gp1 deletions are indicated by pale and dark gray shading, respectively.