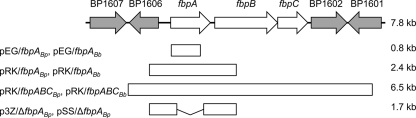
Fig. 3.
Genetic organization of the B. pertussis fbpA chromosomal region. The arrows in the uppermost diagram represent genetic limits and orientations of genes within the B. pertussis Tohama I DNA region that includes the fbpABC genes (white arrows): fbpA (BP1605), ferric iron-binding protein (periplasmic component of an ABC-type Fe3+ transport system); fbpB (BP1604), putative cytoplasmic membrane permease; fbpC (BP1603), probable ATP-binding component of ABC transporter. Flanking genes were as follows: BP1606, putative ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase; BP1607, probable LysR-family transcriptional regulator; BP1602, transposase; BP1601, conserved hypothetical protein. Cloned DNA fragments used for insertional mutagenesis (0.8 kb), complementation (2.4 kb and 6.5 kb), and construction of in-frame fbpA deletion mutations are shown. In B. bronchiseptica, the fragment analogous to the 6.5-kb region is only 5.5 kb in size because this region lacks the IS481 element.