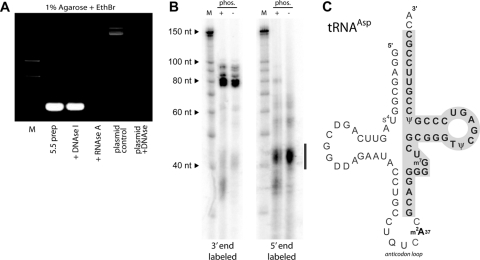
Fig. 7.
The 5.5 protein copurifies with tRNA. (A) After purification by gel filtration chromatography, associated nucleic acid was removed by phenol-choloroform extraction (5.5 preparation) and subsequently treated with DNase I or RNaseA as indicated. The plasmid control shown in the final two lanes demonstrates the activity of the DNase I used in the assay. (B) End labeling of isolated RNA reveals that it is heterogeneous and labels poorly at its 5′ end. Copurifying low-molecular-weight RNA was end labeled at the 3′ end with [32P]pCp and RNA ligase or at the 5′ end with [γ-32P]ATP using T4 polynucleotide kinase. The bar adjacent to the autoradiogram indicates the low-abundance (as determined by Sybr stain), presumably degraded, RNA that was efficiently labeled by PNK. (C) Diagram of tRNAAsp showing, boxed and in bold, the segment obtained by cloning after reverse transcription of in vitro-polyadenylated RNA. Similar truncated clones were obtained from tRNAAla and tRNAThr. EthBr, ethidium bromide; nt, nucleotides.