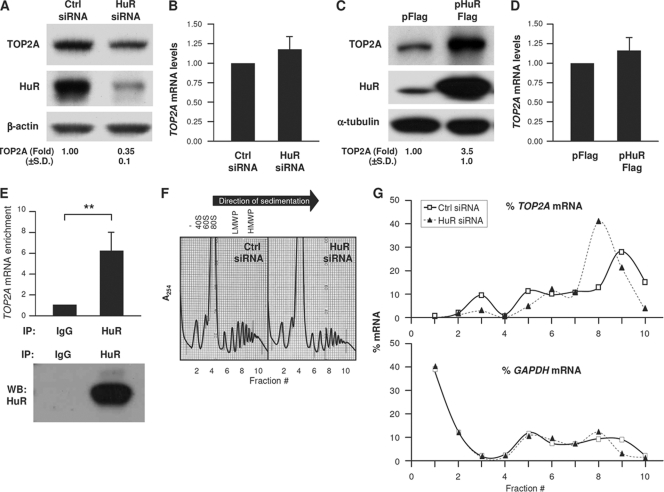
Fig. 1.
HuR associates with TOP2A mRNA and promotes TOP2A translation. (A and B) Forty-eight hours after transfection of HeLa cells with Ctrl siRNA or siRNA targeting HuR (HuR siRNA), Western blot analysis of TOP2A, HuR, and loading control β-actin was performed (A), and the levels of TOP2A mRNA relative to GAPDH mRNA were calculated by RT-qPCR analysis (B). (C and D) Twenty-four hours after transfection of cells with a control (pFlag) or HuR overexpression (pHuR-Flag) plasmid, the levels of TOP2A, HuR, and loading control β-tubulin were assessed by Western blot analysis (C) and TOP2A mRNA/GAPDH mRNA by RT-qPCR analysis (D). (E) RNP IP analysis of the interaction of TOP2A mRNA with HuR using anti-HuR and mouse IgG antibodies. (Top) TOP2A mRNA was detected by RT-qPCR and normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels (see Materials and Methods). (Bottom) Western blot (WB) analysis of HuR in the IP samples. (F and G) Lysates prepared from cells that were transfected as described for panel A were fractionated through sucrose gradients (F), and the relative distribution (%) of TOP2A mRNA and control GAPDH mRNA (G) was studied by RT-qPCR analysis of RNA in each of 10 gradient fractions. The arrow indicates the direction of sedimentation. −, fractions without ribosomal components; 40S and 60S, small and large ribosome subunits, respectively; 80S, monosome; LMWP and HMWP, low- and high-molecular-weight polysomes, respectively. In panels A and C, TOP2A levels were quantified by densitometry; results are shown as the means + standard deviations (SD) (n = 5). In panels B and D, mRNA levels are the means + SD (n = 3). In panels F and G, data are representative of three experiments. **, P < 0.01. For all figures, statistical significance was determined using Student's t test.