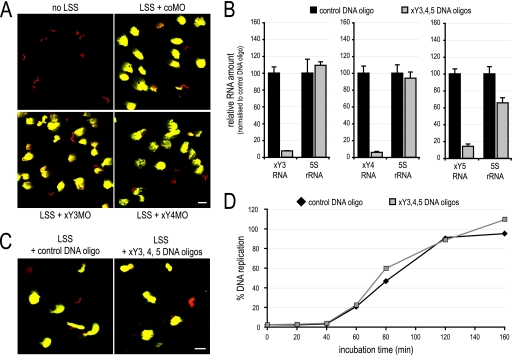
Fig. 7.
DNA replication in Xenopus egg extracts does not require Y RNA function. (A) Nuclear decondensation and DNA replication in the presence of MOs. Xenopus sperm chromatin was incubated in buffer or Xenopus egg extract (low-speed supernatant [LSS]) supplemented with the indicated MOs. DNA replication was analyzed as detailed for Fig. 5B. Bars, 20 μm. (B) Degradation of endogenous xY RNAs. Xenopus egg extract was preincubated in the presence of the indicated DNA antisense oligonucleotides to target RNase H activity to the complementary RNA. Total RNA was prepared from the treated egg extracts, and abundances of the indicated RNAs were determined by qRT-PCR. Data are expressed as percentages of the control-treated extracts. (C) Visualization of nuclear decondensation and DNA replication after Y RNA degradation. Sperm chromatin was incubated in egg extract (LSS) that was pretreated with the indicated DNA antisense oligonucleotides. Data were analyzed as for panel A. (D) Time course of DNA replication in control- and xY RNA-depleted egg extracts. Sperm chromatin was incubated for the indicated time in pretreated egg extracts, and DNA replication was quantified. Incorporation is expressed as the percentage of input template DNA; mean values of two parallel data acquisitions of one representative experiment are shown.