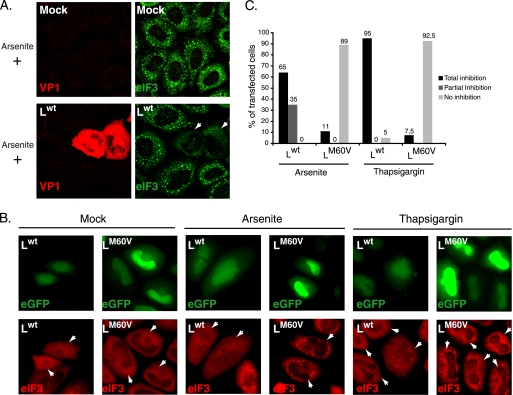
Fig. 4.
Ectopic expression of L is sufficient to inhibit arsenite- or thapsigargin-induced SG assembly. (A) HeLa cells were infected with a wild-type TMEV (Lwt) or with L-mutant viruses (not shown). Twelve hours postinfection, cells were treated with 0.5 mM sodium arsenite for 45 min, fixed, and processed for coimmunolabeling of VP1 and eIF3 (confocal microscopy images). (B) HeLa cells were transfected with bicistronic constructs expressing Lwt and eGFP or LM60V and eGFP. Sixteen hours posttransfection cells were mock treated or treated with 0.5 mM sodium arsenite for 45 min or with 15 μM thapsigargin for 50 min, fixed, and processed for eIF3 immunolabeling. White arrowheads indicate transfected cells. Note that cells transfected with the Lwt-IRES-eGFP construct had a much lower eGFP fluorescence level because Lwt expression represses eGFP expression (30). Moreover, eIF3 exhibited a partially nuclear localization in many cells expressing Lwt, in agreement with the reported effect of this protein on nucleocytoplasmic transport. (C) Histogram showing the percentages of transfected (eGFP-positive) cells displaying total or partial inhibition or no inhibition of arsenite- and thapsigargin-induced SG. In view of ectopically expressed L protein toxicity, only cells with unaltered morphology were taken into account.