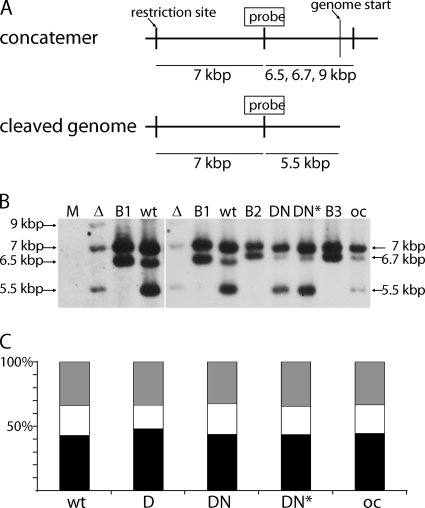
Fig. 8.
Analysis of MCMV DNA cleavage-packaging in pM94 mutant viruses. (A) Schematic representation of the concatemeric and cleaved genome forms. The probe binding site used for Southern blotting as well as the utilized restriction sites, genome starts, and detected fragments are indicated. (B) The detection of different genome fragments in DNA isolated from mock-treated M2-10B4 cells (M) or from cells infected with MCMVΔM94tTA (Δ), MCMVΔ1-16-FRT (wt), or M2-10B4 cells infected with MCMVΔ1-16-RM94i13 in the absence (DN) or presence (DN*) of Dox, as well as MCMVΔ1-16-EHAM94 for overexpression control (oc) is shown. The BACs MCMVΔ1-16-FRT (B1), MCMVΔ1-16-RM94i13 (B2), and MCMVΔ1-16-EHAM94 (B3) served as negative controls. Due to their circular form, digested BAC DNA results in all fragments except the one indicating the cleaved terminal fragments. The left part of the image depicts the same first three lanes also shown in the right image but acquired with an increased exposure time. The sizes for the following fragments are indicated: 7 kbp, loading control fragment; 6.5/6.7/9 kbp, concatemeric fragment; 5.5 kbp, terminal fragment characteristic for the unique length genomes. (C) Quantification of signal intensities. The intensities of individual bands were quantified luminometrically. The ratios of control fragment (black), concatemeric fragment (white), and cleaved genomes (gray) are given as relative intensities in percentages.