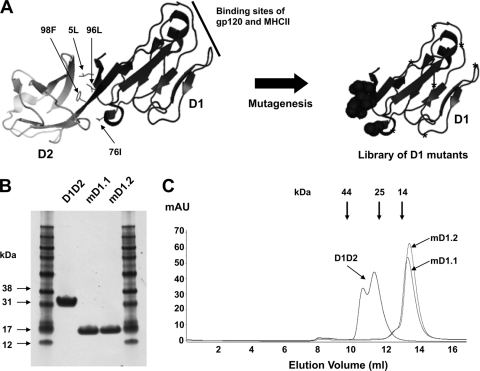
Fig. 1.
Library construction and selection of high-affinity, soluble, stable D1 mutants. (A) Schematic representation of library construction. The X-ray crystal structure of D1D2 (left) was adapted from Protein Data Bank (PDB) 2B4C. The four hydrophobic residues in D1 interacting with D2 are indicated by small arrows. The random-mutagenesis library of D1 is shown on the right, where circles denote randomization of the four hydrophobic residues with the degenerate codon NNS and stars denote randomization by error-prone PCR. (B) Reducing SDS-PAGE of D1D2 and the D1 mutants purified from 293 freestyle cell cultures. (C) Size exclusion chromatography analysis. The thick arrows at the top indicate the elution volumes of molecular mass standards in PBS: RNase A (14 kDa), chymotrypsin (25 kDa), and ovalbumin (44 kDa).