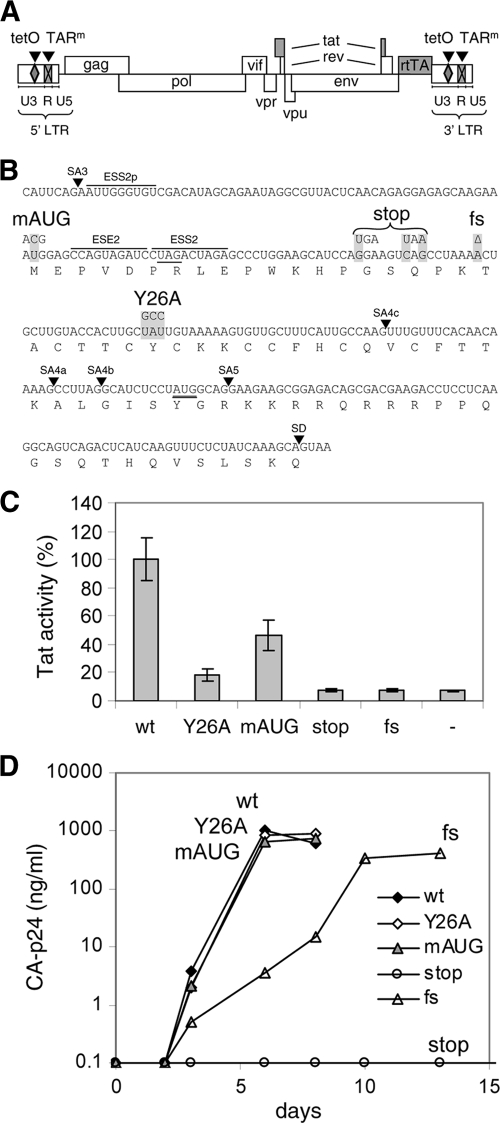
Fig. 1.
Mutations in Tat. (A) Schematic of the HIV-rtTA proviral DNA genome, with the LTR region subdivided in the U3, R, and U5 domains. The Tat-TAR axis of transcription regulation was inactivated by multiple nucleotide substitutions in the bulge and loop sequences of TAR (TARm; crossed boxes). Transcription and replication of the virus were made dox dependent by the introduction of tetO elements in the U3 promoter region and replacement of the Nef gene by the rtTA gene. We constructed different HIV-rtTA variants with either a wild-type or a mutated Tat gene. (B) Mutations in Tat. The sequence of the first Tat-coding exon from splice acceptor 3 (SA3) to the splice donor site (SD) is indicated with the translated amino acid sequence. The mAUG, stop, fs, and Y26A mutations in the Tat gene are boxed in gray. These mutations do not affect the Vpr and Rev amino acid sequences (the Vpr TAG stop codon and the Rev AUG start codon are underlined), splice acceptor (SA) sites, or known splice enhancer (ESE) and silencer (ESS) motifs. (C) Activity of Tat mutants. The HIV-rtTA plasmids and the control plasmid pBluescript (−) were cotransfected with a Tat-responsive HIV-1 LTR promoter/luciferase reporter construct into 293T cells. Luciferase production was measured after the cells were cultured with 1 μg/ml of dox for 48 h. Average values obtained in multiple experiments are shown, with the wild-type level set at 100% and the error bars indicating standard deviations (n = 8 for HIV-rtTA plasmids; n = 4 for pBluescript). Statistical analyses (two-sided unpaired sample t tests) demonstrated that all mutated constructs and the pBluescript control differed significantly from the wild-type construct (P < 0.01). Furthermore, the wt, Y26A, and mAUG constructs differed significantly from the pBluescript control, while the stop and fs mutants did not. (D) Replication of HIV-rtTA variants. SupT1 T cells were transfected with the different HIV-rtTA plasmids and cultured with 1 μg/ml of dox. CA-p24 levels in the culture supernatants were measured by ELISA. No virus replication was observed in the absence of dox (data not shown). The replication curves shown are representative of data obtained in four experiments.