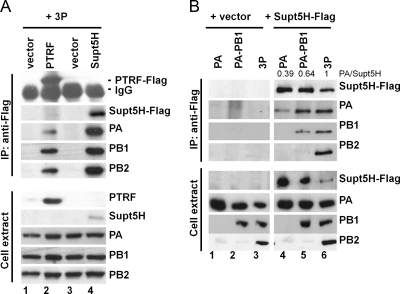
Fig. 9.
Interaction of Supt5H and PTRF with the viral polymerase complex and polymerase subunits in transfected HEK293T cells. (A) To confirm the interaction between Supt5H and PTRF to the 3P complex by coimmunoprecipitation experiments, HEK293T cells were transfected with expression constructs (0.2 μg) encoding PTRF-Flag (lane 2), Supt5H (lane 4), or empty vector (lanes 1 and 2) and the components of the VN/1203 (H5N1) polymerase complex (PA, PB1, and PB2) (0.6 μg each). Whole-cell extract was prepared at 24 h posttransfection and used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with Flag-specific rabbit polyclonal antibody. The presence of Supt5H-Flag and PTRF-Flag, PA, PB1, and PB2 in the precipitates (upper panel) as well as cell extract (lower panel) was analyzed by Western blotting using Flag and polymerase-specific antibodies. Approximately 3% of total cell extract used for IP was loaded. (B) Flag-tagged Supt5H expression vector (lanes 4 to 6) or empty vector (lanes 1 to 3) was transfected into HEK293T cells with plasmid vector encoding PA alone, PA and PB1, or 3P from the VN/1203 strain (H5N1). Whole-cell extract was prepared 24 h posttransfection and used for immunoprecipitation with Flag-specific rabbit polyclonal antibody. The presence of Supt5H-Flag and PA, PB1, and PB2 in the precipitates (upper panel) as well as cell extract (lower panel) was analyzed by Western blotting using Flag and polymerase-specific antibodies. Approximately 3% of total cell extract used for IP was loaded. Numbers at the top of lanes 4 to 6 denote the relative ratios of PA to Supt5H, as determined by densitometric analysis of the immunoprecipitates.