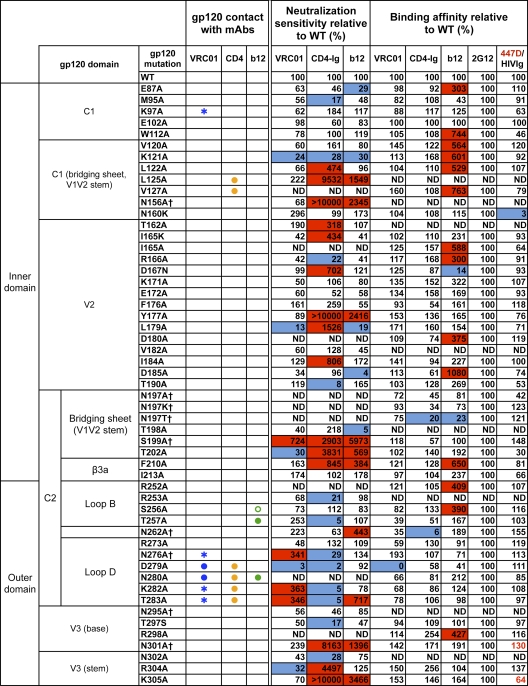
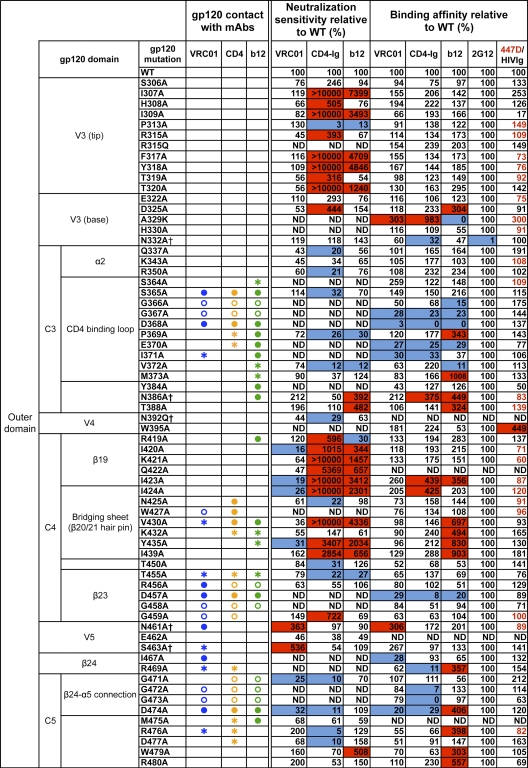
Fig. 1.
VRC01 neutralization and binding on a panel of primary isolate JRCSF functional Env and gp120 mutants. Amino acid numbering of mutants is based on the HIV-1 HXBc2 sequence. The gp120 structurally defined contact residues for the VRC01, CD4, and b12 complexes are indicated in blue, orange, and green, respectively, with open circles (○) designating gp120 main-chain-only contacts, asterisk (*) designating gp120 side chain-only contacts, and filled circles (●) designating both main-chain and side-chain contacts. Mutations that knock out putative N-glycosylation sites (NXS/T motifs) of gp120 are labeled with a dagger symbol (†). Relative ELISA binding affinities to captured gp120s were calculated based on the antibody concentration at half-maximal binding (EC50). The effect of each mutation on antibody binding was normalized using 2G12 to control for the amount of captured gp120. Mutations that resulted in decreased gp120 binding (<33% relative to that of wild type [WT]) are highlighted in blue, and those that resulted in increased ELISA binding (>300% relative to that for the wild type) are highlighted in red. HIVIg or the anti-V3 MAb 447D (values shown in red) were used as the controls for gp120s with poor 2G12 binding. Neutralization sensitivity of each mutant to MAb VRC01, CD4-Ig, or MAb b12 was assessed and compared to neutralization of the wild-type Env pseudovirus. The color scheme is the same as that used for the gp120 binding data.