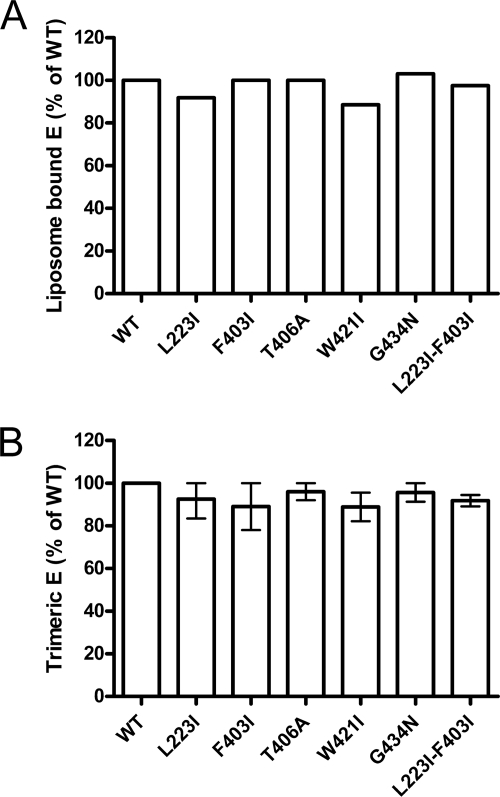
Fig. 2.
Low-pH-induced coflotation (A) and E protein trimerization (B) of WT and mutant RSPs. (A) RSPs were exposed to acidic pH in the presence of liposomes, back-neutralized, and subjected to sucrose step gradient centrifugation. The gradients were fractionated, and the amount of E protein in each fraction was determined by a quantitative four-layer ELISA. Results are expressed as a percentage of E found in the top fractions relative to the WT (set to 100%). (B) RSPs were exposed to acidic pH, back-neutralized, solubilized, and subjected to sedimentation in sucrose gradients. The gradients were fractionated, and the amount of E protein in each fraction was determined by a four-layer ELISA. Results are expressed as a percentage of E present in the trimer peak fractions relative to the WT (set to 100%). The data display the means of data from two independent experiments, and the error bars represent the observed ranges.