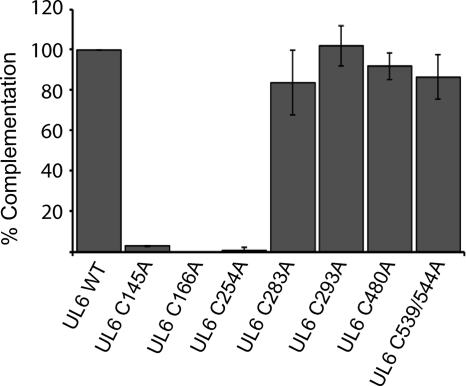
Fig. 4.
Cysteine-to-alanine substitutions at positions 145, 166, and 254 abolish complementation ability. Alanine substitution mutations were made at each of the cysteine residues. A transient complementation assay was used to determine the ability of the substitution mutants to complement the null virus hr74. Vero cells were transfected with plasmid DNAs bearing cysteine-to-alanine mutations and superinfected with hr74 virus, and the titer of the resulting progeny virus was determined on UL6-31 cells. This experiment was repeated three times. Error bars represent standard deviations.