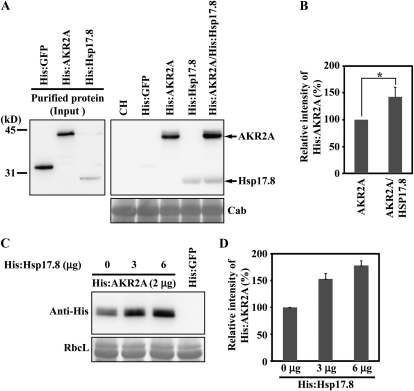
Figure 5.
Hsp17.8 increases the amount of AKR2A proteins bound to chloroplasts. A and B, The effect of Hsp17.8 on the AKR2A binding to chloroplasts. A, His-tagged AKR2A or Hsp17.8 recombinant proteins were expressed in E. coli and purified using a nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid agarose affinity column (left panel). Purified recombinant proteins (2 μg) were incubated with intact chloroplasts purified from protoplasts. His:GFP (2 μg) was included as a control. After incubation on ice, chloroplasts were pelleted and proteins from the pellet fraction were analyzed by western blotting using anti-His antibody. As a control, 10% of total proteins (10%) was included in the western blotting. Subsequently, the blot was stained with Coomassie blue and chlorophyll a/b-binding protein (Cab) was used as a loading control. CH, Extracts from chloroplasts. B, To quantify the binding, the intensity of His:AKR2A and His:HSP17.8 was quantified using software equipped on the LAS3000 and is presented as relative values to the controls (His:AKR2A alone or His:HSP17.8 alone). AKR2A, His:AKR2A; HSP17.8, His:HSP17.8. The asterisk denotes a statistically significant difference compared with His:AKR2A alone (P < 0.01; n = 3). Error bars represent se (n = 3). C and D, The effect of Hsp17.8 concentrations on AKR2A binding to chloroplasts. C, Varying amounts of His:Hsp17.8 were incubated with a fixed amount of His:AKR2A (2 μg) and purified chloroplasts. Chloroplast-bound proteins were pelleted by low-speed centrifugation. His:GFP was used as a negative control for His:AKR2A. Pelleted proteins were analyzed by western blotting using anti-His antibody. Total proteins (10%) were included in the western-blot analysis. RbcL, Large subunit of the Rubisco complex, used as a loading control. D, To quantify binding, His:AKR2A intensity was measured and is presented as relative values to the control, His:Hsp17.8 (0 μg).