Figure 1.
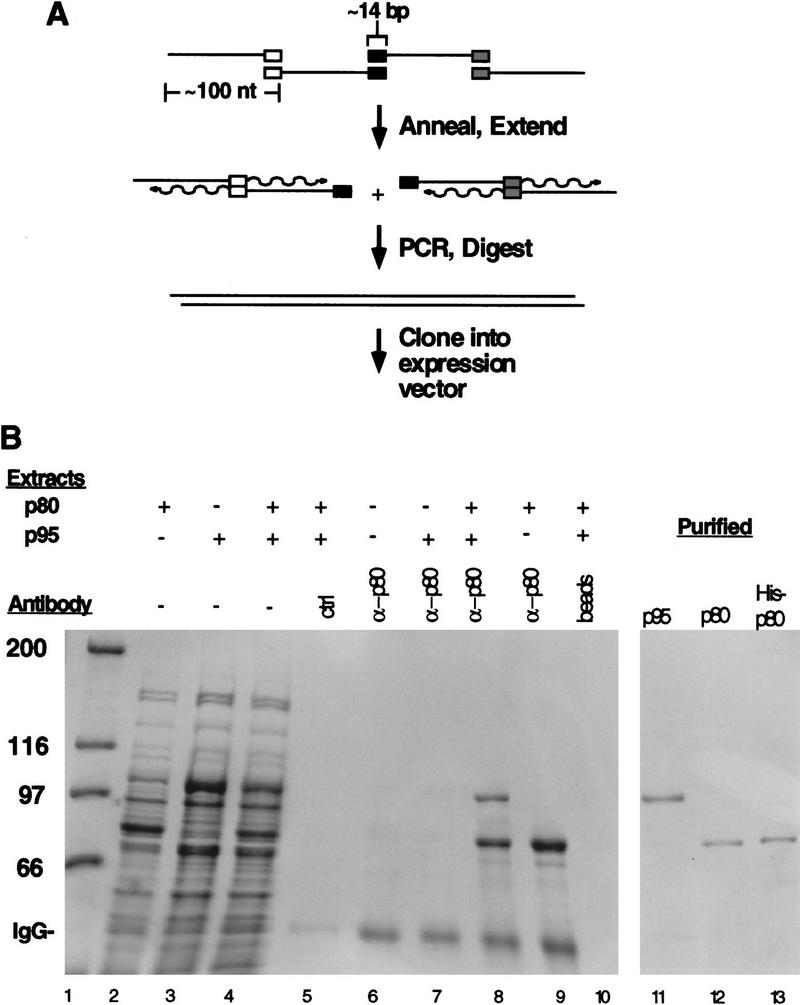
Gene construction, expression, and purification of p80 and p95. (A) Oligonucleotides of ∼100 nucleotides with an overlap of ∼14 bp were annealed and extended in pairs. Pairwise extension reactions were pooled and amplified by PCR to generate DNA for restriction digestion and cloning. (B) E. coli extracts from cells expressing p80 (lane 2), p95 (lane 3), or mixed p80 and p95 extracts (lane 4) were used in immunoprecipitation reactions. Antibodies were covalently coupled to CNBr-activated Sepharose at equivalent concentrations for these experiments; p80 antibody beads alone are shown in lane 6. Some antibody was dissociated from the resin in reducing SDS-PAGE loading buffer, migrating at the position indicated by IgG. Anti-p80 beads were used to immunoprecipitate from p95 extract (lane 7), mixed p80 and p95 extracts (lane 8), or p80 extract (lane 9). Control reactions included an antibody raised against an unrelated protein that was used to immunoprecipitate from mixed p80 and p95 extracts (lane 5) and Sepharose beads used to immunoprecipitate from the same mixed extracts in the absence of binding and conjugation of p80 antibodies (lane 10). The three purified proteins used in this study are shown in lanes 11–13. (Lane 1) Molecular mass markers indicated at left in kD.
