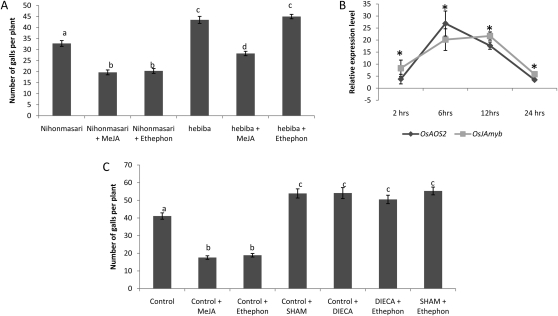
Figure 5.
A, Effects of JA/ET-induced systemic defense against M. graminicola in the JA biosynthesis mutant hebiba and the corresponding wild-type Nihonmasari. B, qRT-PCR data showing the relative expression levels of JA biosynthesis (OsAOS2) and signaling (OsJAmyb) genes in the roots at different time points after systemic exogenous ET supply in wild-type plants. C, JA/ET-induced systemic defense after application of JA biosynthesis-inhibitors SHAM and DIECA. Fifteen-day-old plants were sprayed until runoff with 500 μm ethephon, 100 μm MeJA, or the control solution and with or without SHAM (200 μm) and DIECA (100 μm). Plant roots were inoculated with 300 M. graminicola juveniles. Bars represent means and se of the number of galls at 2 weeks after inoculation recorded on eight plants. For infection experiments, different letters indicate statistically significant differences (Duncan’s multiple range test with α = 0.05). For qRT-PCR data, asterisks indicate significant differential expression in comparison with untreated control tissue. Data represent one of two independent experiments with similar results.