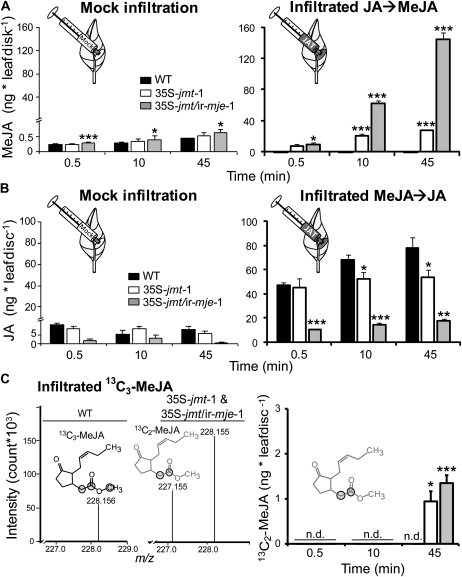
Figure 2.
N. attenuata 35S-jmt and 35S-jmt/ir-mje plants have altered JA-methylation and MeJA-demethylation activities. Leaf discs (0.4 cm2) were infiltrated with a control solution (Mock) and 0.5 μg of JA (A), unlabeled MeJA (B), or 0.25 μg synthetic MeJA labeled with 13C ([1, 2, 13-13C]MeJA; C). JA methylation (A), MeJA demethylation (B), and the remethylation of the subsequently released JA (C) were analyzed by quantifying 0.5, 10, and 45 min increases (mean ± sd, n = 5) in MeJA (JA → MeJA), JA (MeJA → JA), and [1, 2-13C]MeJA levels after infiltration in the elicited leaves. After JA infiltration, 35S-jmt-1 and 35S-jmt/ir-mje-1 leaves showed larger MeJA accumulations than wild type that came at the expense of other JA metabolites (Supplemental Fig. S2). MeJA deesterification was strongly impaired in 35S-jmt/ir-mje-1 and only slightly reduced in 35S-jmt-1 plants. Left section of C: high-resolution time-of-flight MS measurement of (calculated m/z = 228.158) [1, 2, 13-13C]MeJA-infiltrated leaf areas—zoom in of the spectral range m/z 227 to 229—revealed the production of a m/z signal at 227.155 characteristic for 13C2-MeJA ([1, 2-13C]MeJA, calculated m/z = 227.155) formed by remethylation of the deesterified 13C3-MeJA in 35S-jmt-1 and 35S-jmt/ir-mje-1, but not in wild-type leaf samples. 13C atoms are circled. Right section of C: [1, 2-13C]MeJA levels. Asterisks represent significant differences between wild-type and transgenic lines (unpaired t test; * P < 0.05, ** < 0.001, *** < 0.0001). n.d., Not detected.