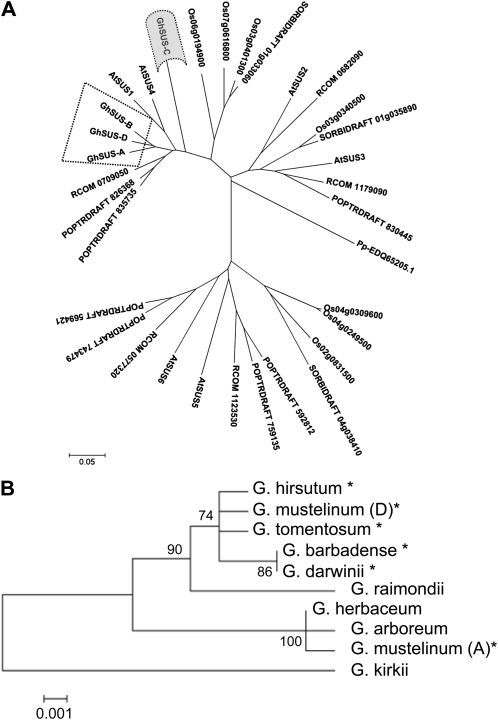
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of Sus protein sequences generated using MEGA 4.0 and the neighbor-joining method (see “Materials and Methods”). A, Unrooted tree of 28 plant Sus proteins from plants with sequenced genomes: the dicots Arabidopsis (AtSUS1 to -6), Populus trichocarpa (POPTRDRAFT), and Ricinus communis (RCOM_xxxxxxx), the monocots Oryza sativa japonica group (Osxxxxxxxx) and Sorghum bicolor (SORBIDRAFTxxxxxxxx), together with the four cotton Sus proteins reported in this paper, and with the moss (Physcomitrella patens subspecies patens) Sus protein (Pp-EDQ65205.1) as an outgroup. The cotton Sus proteins are surrounded by dotted lines, and the SusC protein is shaded in gray (alignment files are provided as Supplemental Fig. S1). B, Phylogenetic tree of the SusC proteins from selected diploid and tetraploid Gossypium species (alignment files shown in Supplemental Fig. S2). The G. kirkii SusC sequence was used as the outgroup. Tetraploid cotton species names are indicated by asterisks. The numbers on the interior branches refer to the bootstrap values for 1,000 replications. Bootstrap values less than 50% are not given. The scale at the bottom is in units of amino acid substitutions per site.