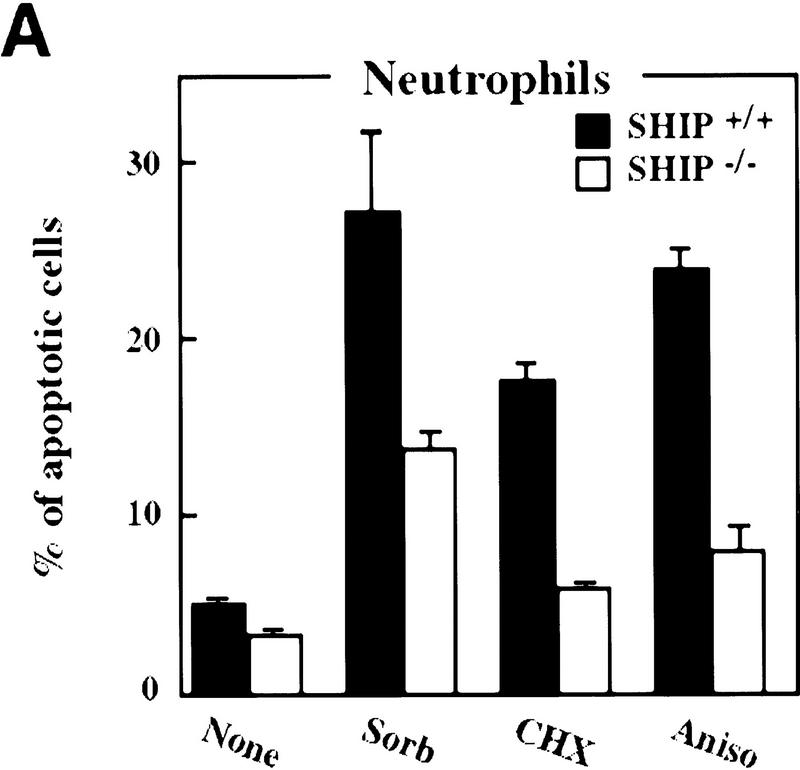
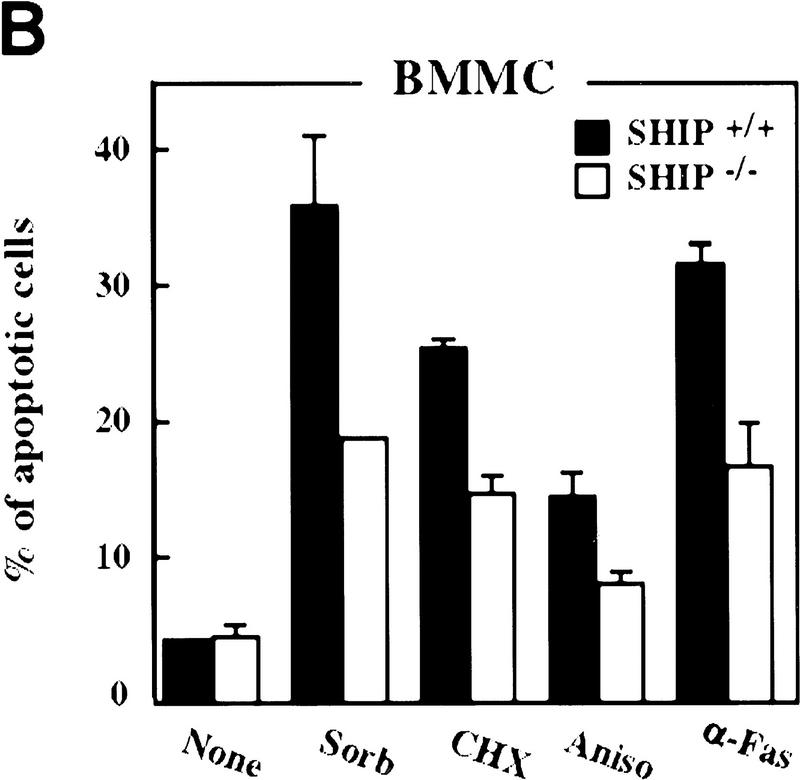
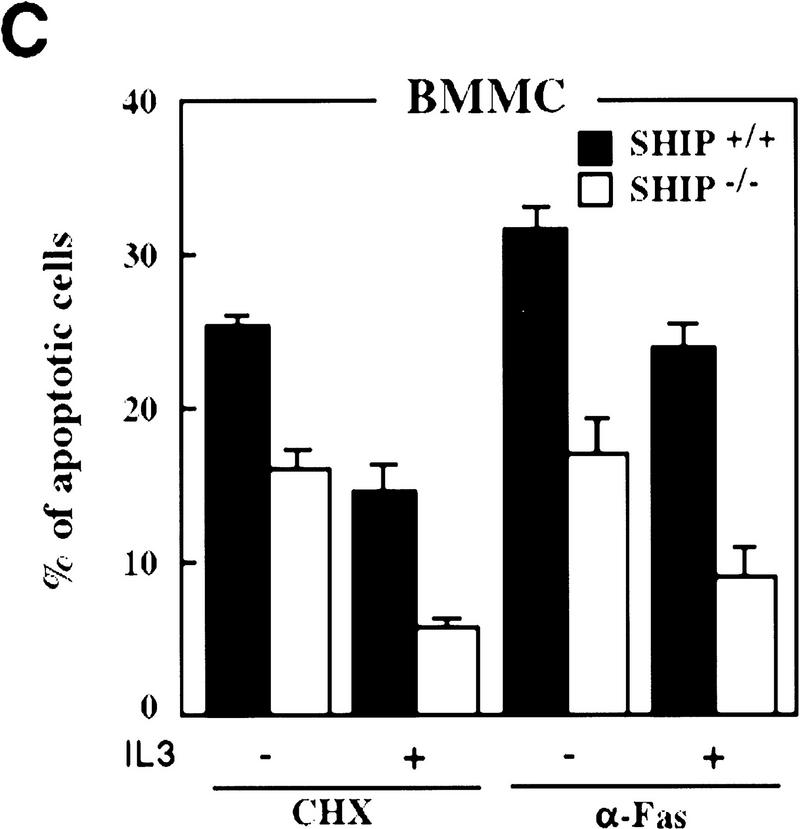
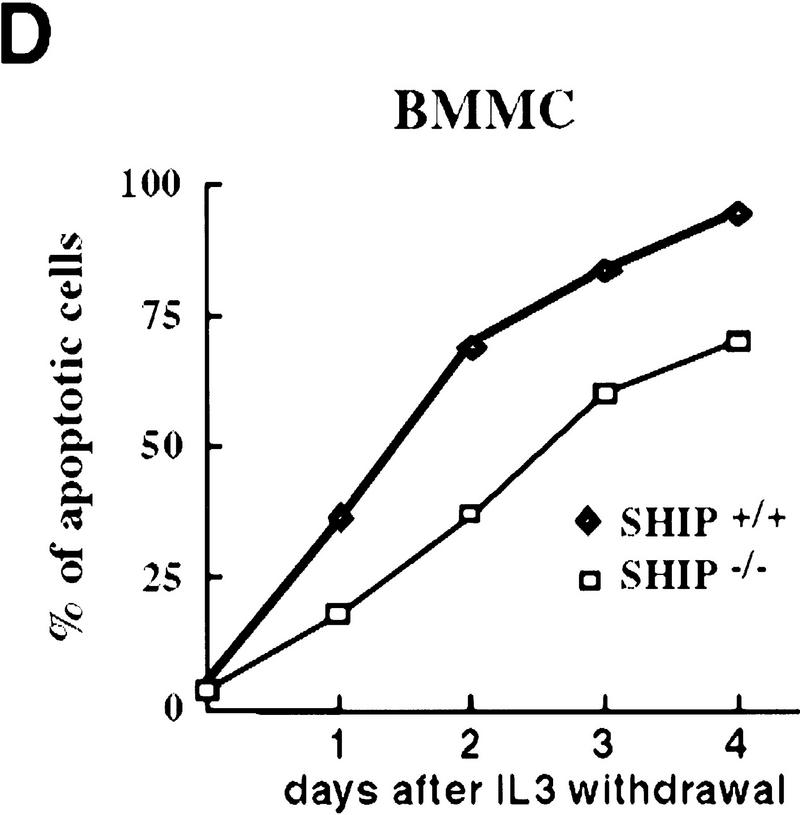
Figure 2.
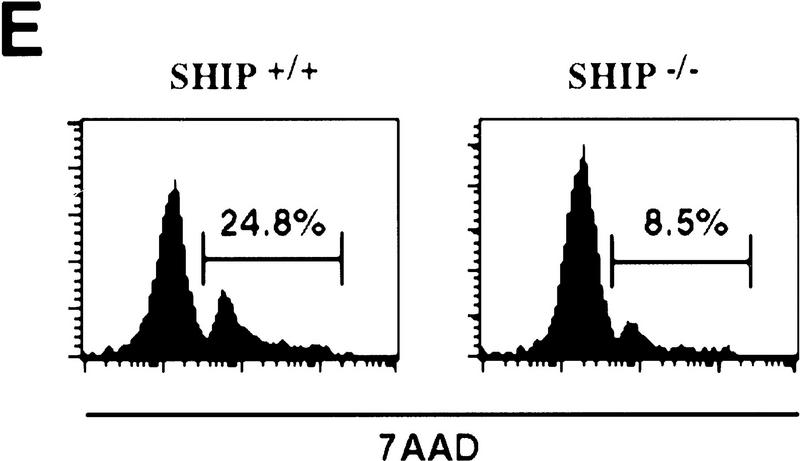
Decreased sensitivity of SHIP-deficient myeloid cells to apoptotic stimuli. Freshly isolated neutrophils (A)and BMMCs derived from SHIP+/+ and SHIP−/− mice (B) were incubated with PBS (none); 400 mm sorbitol (Sorb), 50 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX), 2 μg/ml anisomycin (Aniso), or 2 μg/ml anti-Fas antibody (α-Fas) as indicated. The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined 24 hr after death using 7AAD. (C) IL3 increases the survival of SHIP+/+ and SHIP−/− BMMCs. BMMCs were incubated with or without IL3 in the presence of the indicated apoptotic stimuli. Percentages of apoptotic cells were determined 24 hr after induction. Genotypes of cells are indicated. Percentages of apoptotic cells were determined by staining with 7AAD. (A–C) are representative of at least five independent experiments. Percentages of survival and mean values of triplicate cultures ± s.e.m. are shown. (D) IL3-dependent BMMCs from SHIP−/− mice show higher viability following IL3 withdrawal. IL3 was removed and BMMCs were incubated in 2% FBS. The viability of cells was monitored for 4 days using 7AAD staining. One experiment is representative of five independent experiments. (E) Representative flow cytometric analysis showing the percentages of 7AAD-positive apoptotic cells in SHIP+/+ and SHIP−/− BMMCs 24 hr after IL3 withdrawal as in D.