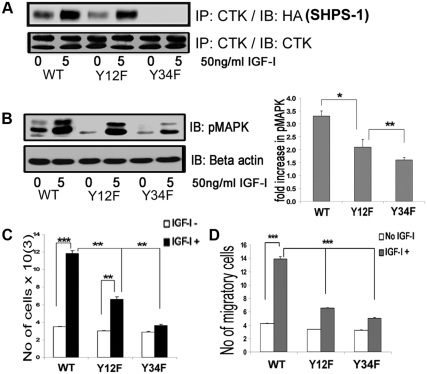
Fig. 5.
Substitution for specific tyrosines on SHPS-1 alters CTK association and IGF-I signaling-stimulated actions. A, Confluent VSMC expressing SHPS1-WT and SHPS1 (Y12F and Y34F) mutant cells were serum starved for 16 h in DMEM-HG and then exposed to IGF-I for 5 min. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-CTK antiserum then immunoblotted (IB) for HA-tagged SHPS-1. An equal amount of protein from cell lysates was used for IP/IB to estimate total CTK. B, Twenty micrograms of protein from the same cell lysates were directly immunoblotted with anti-pMAPK or anti-β-actin. Error bars represent mean ± se. *, P < 0.05 when phosphorylation of MAPK at 5 min in response to IGF-I is compared between WT and Y12F; **, P < 0.01 when Y12F and Y34F are compared. C, SHPS-1-WT, Y12F, and Y34F cells were plated (3 × 104) in DMEM-HG with 2% FBS before exposure to IGF-I (50 ng/ml) in DMEM-HG with 0.2% platelet-poor plasma. Forty-eight hours after the addition of IGF-I, the cell number was determined by tryptan blue staining and counting. The bar graphs show pooled results from at least three independent experiments. Error bars represent mean ± se. ***, P < 0.001 when the increase in cell number cell number in response to IGF-I in WT cells is compared with control; **, P < 0.01 when increase in cell number in response to IGF-I in Y12F cells is compared with control; **, P < 0.01 when the increases in cell number between WT and Y12F cells or between Y12F and Y34F cells are compared. D, SHPS-1 WT, Y12F, and Y34F cells were grown to confluent density in six-well plates in DMEM-HG containing 10% FBS. After wounding, they were allowed to migrate with or without IGF-I in medium containing 0.2% FBS for 48 h. The total number of cells migrating past the wound edge in five predetermined areas was quantified. ***, P < 0.001 when the number of WT cell migration in response to IGF-I is compared with control or with the number of migration of Y12F or Y34F cells.