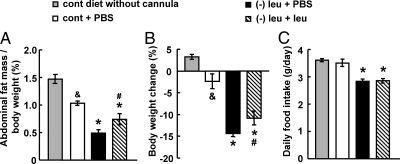
Fig. 1.
Intracerebroventricular administration of leucine significantly attenuates abdominal fat loss in leucine-deprived mice. A–C, Mice received icv administration of leucine (1.1 μg of leucine in 1.0 μl of PBS) or PBS once a day for 7 d under a control (cont) or (−) leu diet. Data are mean ± sem for at least two independent experiments with mice maintained on each diet for each experiment (n = 8–11 for each group). Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA followed by the SNK test for the effect of control diet with icv PBS vs. without cannula implantation (&, P < 0.05), (−) leu diet with icv PBS or leucine vs. control diet with icv PBS (*, P < 0.01), or (−) leu diet with icv leucine vs. (−) leu diet with icv PBS (#, P < 0.05). A, Adipose tissue mass in proportion to body weight. B, Body weight change. C, Daily food intake.