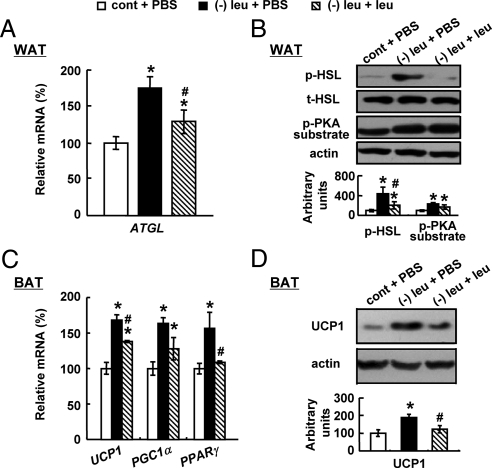
Fig. 2.
Intracerebroventricular administration of leucine prevents changes in WAT and BAT in leucine-deprived mice. Mice received icv administration of leucine (1.1 μg of leucine in 1.0 μl of PBS) or PBS once a day for 7 d under a control or (−) leu diet. Data are mean ± sem for at least two independent experiments with mice maintained on each diet for each experiment (n = 8–11 for each group). Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA followed by the SNK test for the effect of (−) leu diet with icv PBS or leucine vs. control diet with icv PBS (*, P < 0.01), or (−) leu diet with icv leucine vs. (−) leu diet with icv PBS (#, P < 0.05). A, Atgl mRNA expression in WAT. B, p-HSL and p-PKA substrate protein in WAT (upper, Western blotting; lower, quantitative measurements of p-HSL and p-PKA substrate protein relative to total (t)-HSL and actin, respectively). C, Ucp1, Pparγ, and Pgc1α mRNA expression in BAT. D, UCP1 protein in BAT.