Figure 4.
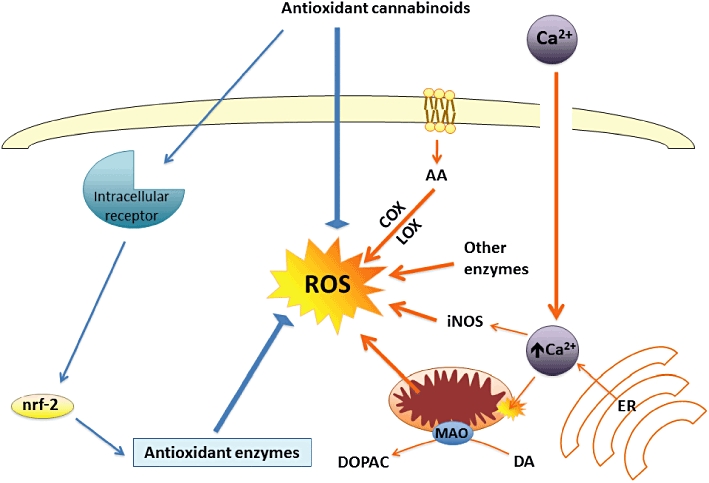
Mechanisms proposed for the neuroprotective effects exerted by cannabinoids against oxidative injury that occurs in most neurodegenerative disorders, including HD and PD. These neuroprotective effects involve mainly CB1 and CB2 receptor-independent mechanisms. COX, cyclooxygenase; DA, dopamine; DOPAC, dihydroxyphenylacetic acid; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LOX, lipoxygenase; MAO, monoamine oxidase; nrf-2, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
