Figure 5.
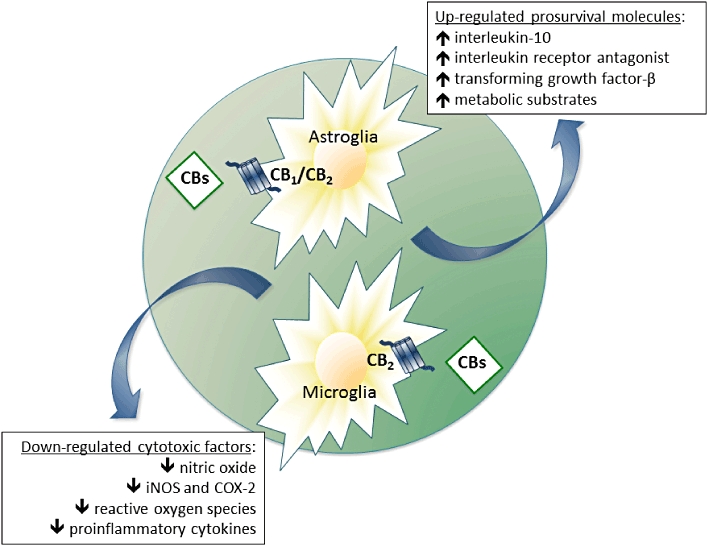
Mechanisms proposed for the neuroprotective effects exerted by cannabinoids against inflammatory events that occur in most neurodegenerative disorders, including Huntington's disease and Parkinson's disease. These neuroprotective effects involve mainly the activation of CB2 receptors located in glial cells (reactive microglia and/or astrocytes). COX-2: cyclooxygenase type-2; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide.
