Figure 7.
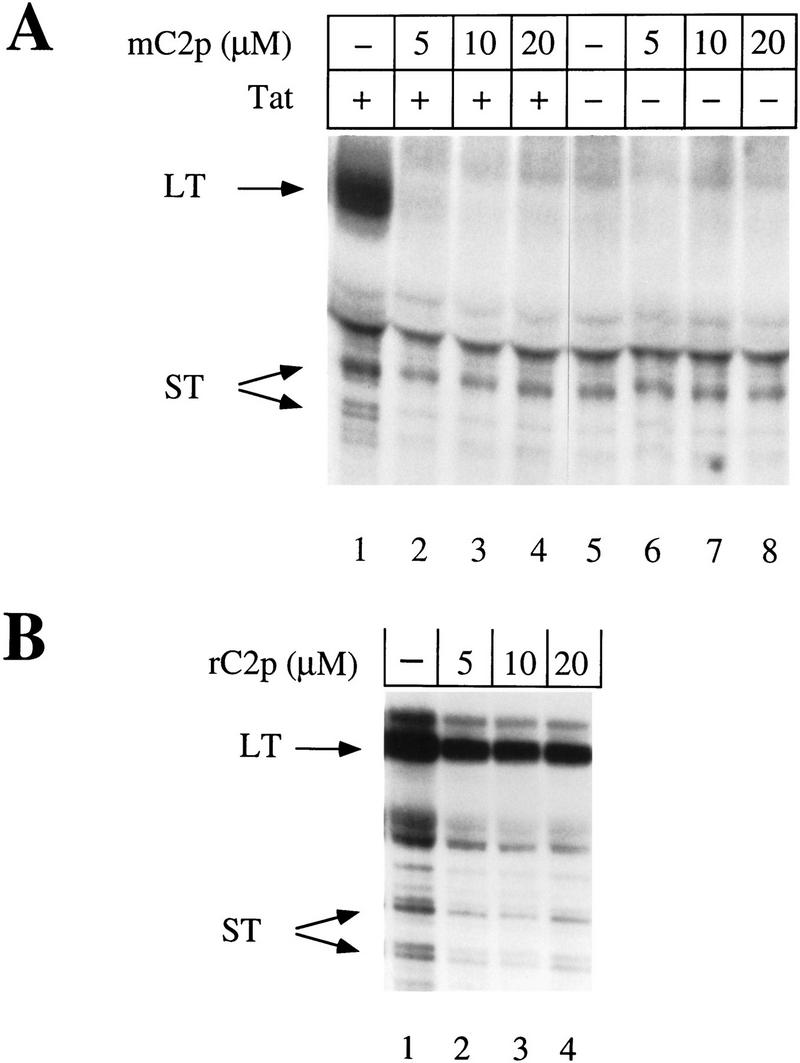
The mutant CDK2 peptide inhibits Tat transactivation in vivo. (A) Increasing concentrations of the mutant CDK2 peptide (mC2p) were cotransfected into COS cells with a reporter plasmid containing HIV LTR promoter sequences that lacked NF-κB-binding sites (pHIVΔKBCAT) and either functional (+) or nonfunctional (−) Tat. RNase protection assays were done with a probe 220 nucleotides long and hybridized to full-length transcripts of 80 nucleotides (LT) or prematurely terminated transcripts (ST) of 55–59 nucleotides (Okamoto et al. 1996). Protected fragments were resolved on a 11% polyacrylamide/urea sequencing gel and exposed to x-ray film after drying. (B) Increasing concentrations of the randomized CDK2 peptide (rC2p) were cotransfected into COS cells with a reporter plasmid containing the HIV LTR lacking NF-kB-binding sites (pHIVΔKBCAT) and functional Tat. RNase protection assays were done as in A.
