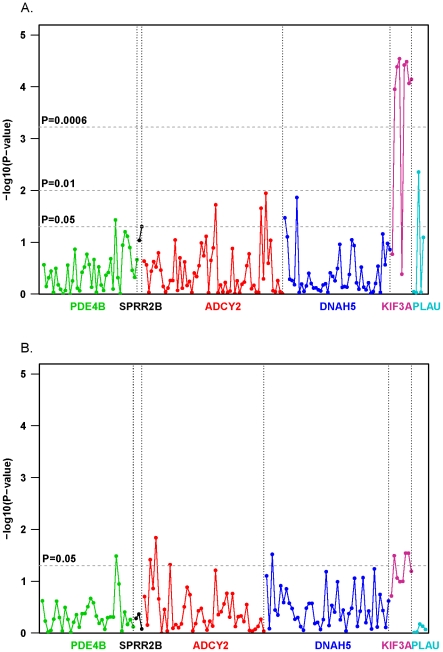
Figure 2. Genetic associations with childhood asthma.
A. We evaluated associations in our discovery Caucasian population between asthma and 160 directly genotyped SNPs within the six epithelial genes using the additive model after adjusting for age and gender. The upper dashed line corresponds to a p-value of 0.0006, the Bonferroni adjustment after considering LD correlation between SNPs. SNPs significant at this level (all in KIF3A) include rs12186803 (p = 0.00011), rs3798130 (p = 0.00004), rs2299011 (p = 0.00003), rs12514685 (p = 0.00004), rs7737031 (p = 0.00003), rs1080001 (p = 0.00009), and rs9784675 (p = 0.00007). The lower dashed line corresponds to a p-value of 0.05. SNPs significant at this level include rs11747117 (p = 0.0188), rs7714830 (p = 0.0219), and rs13174121 (p = 0.0113) in ADCY2, rs2896111 (p = 0.0335) and rs17263496 (p = 0.0136) in DNAH5, rs12060491 (p = 0.0369) in PDE4B, rs6693927 (p = 0.0496) in SPRR2B and rs2227562 (p = 0.0044) in PLAU. B. Associations between asthma and 160 directly genotyped SNPs within the six epithelial genes were evaluated among African American children from Cincinnati using an additive model after adjusting for age and gender. The dashed line corresponds to a p-value of 0.05. SNPs significant at this level include rs11742602 (p = 0.038), rs2017214 (p = 0.014) and rs1032719 (p = 0.048) in ADCY2, rs30168 (p = 0.030) in DNAH5, rs11208834 (p = 0.032) in PDE4B, rs12186803 (p = 0.032), rs1080001 (p = 0.029) and rs7737031 (p = 0.028) in KIF3A.