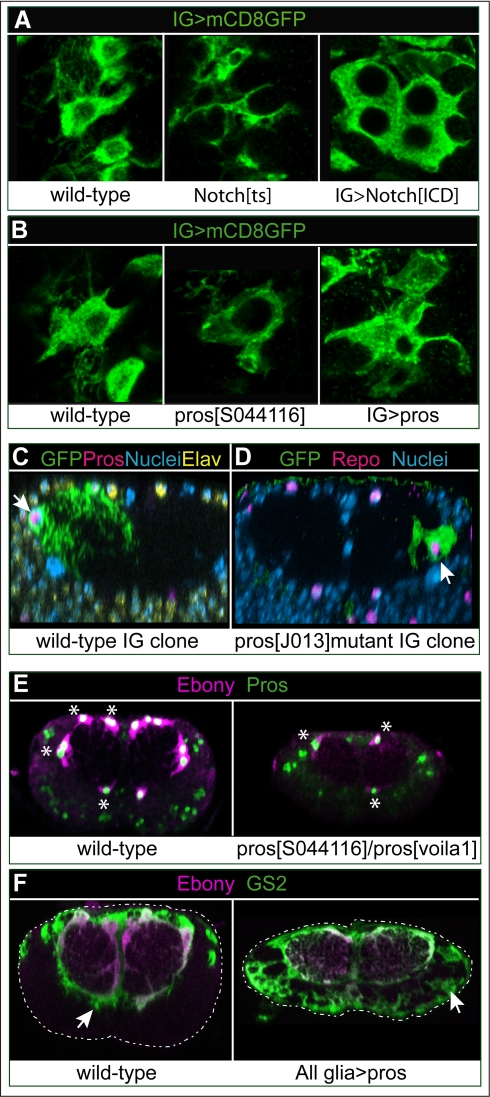
Figure 7. Pros promotes glial differentiation.
(A,B) Notch and Pros have opposite effects in glial differentiation, seen here using membrane targeted mCD8GFP expressed by the IG driver alrmGAL4 and detected with anti-GFP. (A) Glial differentiation is influenced by Notch, as filopodia and lamellipodia are thin in Notchts1 mutants, and cells are large and round up upon the over-expression of NotchICD. (B) Pros is necessary for glial differentiation, as there is loss of IG filopodia in prosS044116 mutants and more filopodia upon over-expression of pros. (C,D) Loss of pros does not affect glial number but prevents glial differentiation. Wild-type (C) and (D) prosJ013 null mutant MARCM clones showing that the number of progeny cells in a prosJ013 mutant clone (arrow) did not differ from the number of cells in a wild-type clone (quantification in text), while glial projections were deficient in the pros mutant clone, meaning that Pros is necessary for glial differentiation. Transverse views, nuclear dye is DAPI. (E) Ebony is virtually lost in pros hypomorphic mutants, and residual Ebony colocalises with residual Pros protein (asterisks). This shows that Ebony is a downstream differentiation target of Pros. (F) Over-expression of pros induces the expression of GS2, a differentiation marker for enwrapping glia (left image, arrow), in non-enwrapping glia outside the neuropile (right image, arrow indicates cortex glia). Dashed line indicates edges of the VNC, which was smaller in pros mutants. Genotypes from left to right: (A) (1) w;alrmGAL4/UASmCD8GFP, (2) Notchts1/Y;alrmGAL4/UASmCD8GFP, and (3) w;UASmCD8GFP/+;alrmGAL4/UASNotchICDmyc. (B) (1) w;alrmGAL4/UASmCD8GFP, (2) w;alrmGAL4/UASmCD8GFP; prosS044116/prosS044116, and (3) w;UASpros/UASmCD8GFP; alrmGAL4/+. (C) (1) hsFLP tubP-GAL80 FRT19A/FRT19A; repoGAL4/UASmCD8GFP, and (2) hsFLP;actGAL4, UASGAPGFP/+;neoFRT82B tubGAL80/neoFRT82B prosJO13F263. (F) (1) w;tubGAL80ts/+;repoGAL4/+., and (2) w;UASpros/tubGAL80ts; repoGAL4/+.