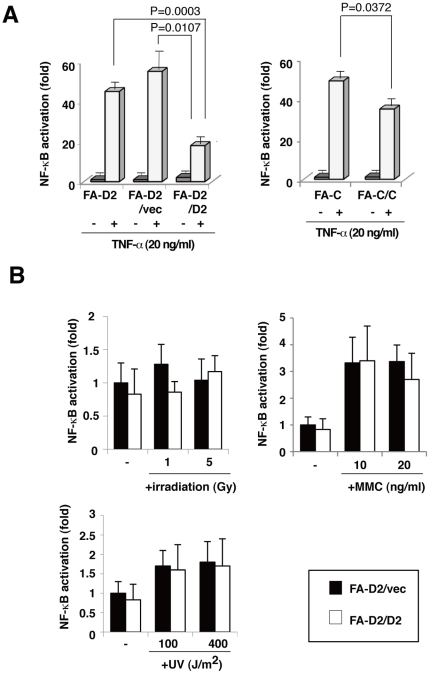
Figure 1. Deficiency of FANCD2 increases TNF-α-induced NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity.
(A) FA fibroblast cells derived from complementation group C and group D2 patients were designated FA-C (PD331) and FA-D2 (PD20), respectively. FA-C/C (FA-C; (PD331)+FANCC) and FA-D2/ D2 (FA-D2; (PD20)+FANCD2) were retrovirus-transformed derivatives of PD331 and PD20 that expressed functional FANCC and FANCD2, respectively. FA-D2/vec cells (FA-D2 expressing empty vector) were FANCD2-deficient derivatives of PD20. FA-D2 cells (FA-D2 and FA-D2/vec) showed higher TNF-α-induced NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity than did the FANCD2-expressing cells (FA-D2/D2); similarly FANCC-deficient cells (FA-C) exhibited more NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity than did FANCC-expressing cells (FA-C/C). FA fibroblasts were transfected with pNFκB-Luc (100 ng) and pRL-CMV (10 ng). Cells were treated with or without TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 8 h. Cells were harvested and dual luciferase assays were performed. Fold activation represents the mean (± s.d) luciferase values of indicated cells normalized with respect to unstimulated FA-D2 cells, from three independent experiments. (B) FANCD2 did not have a significant effect on irradiation-, MMC- or UV-induced NF-κB activation. FA-D2 and FA-D2/D2 fibroblast cells were transfected with pNFκB-Luc (100 ng) and pRL-CMV (10 ng). Cells were treated with irradiation (1. 5 Gy), MMC (10, 20 ng/ml) or UV (100, 400 J/m2). Fold activation represents the mean (± s.d) luciferase values of indicated cells normalized with respect to un-stimulated FA-D2/vec cells, from three independent experiments.