Figure 5.
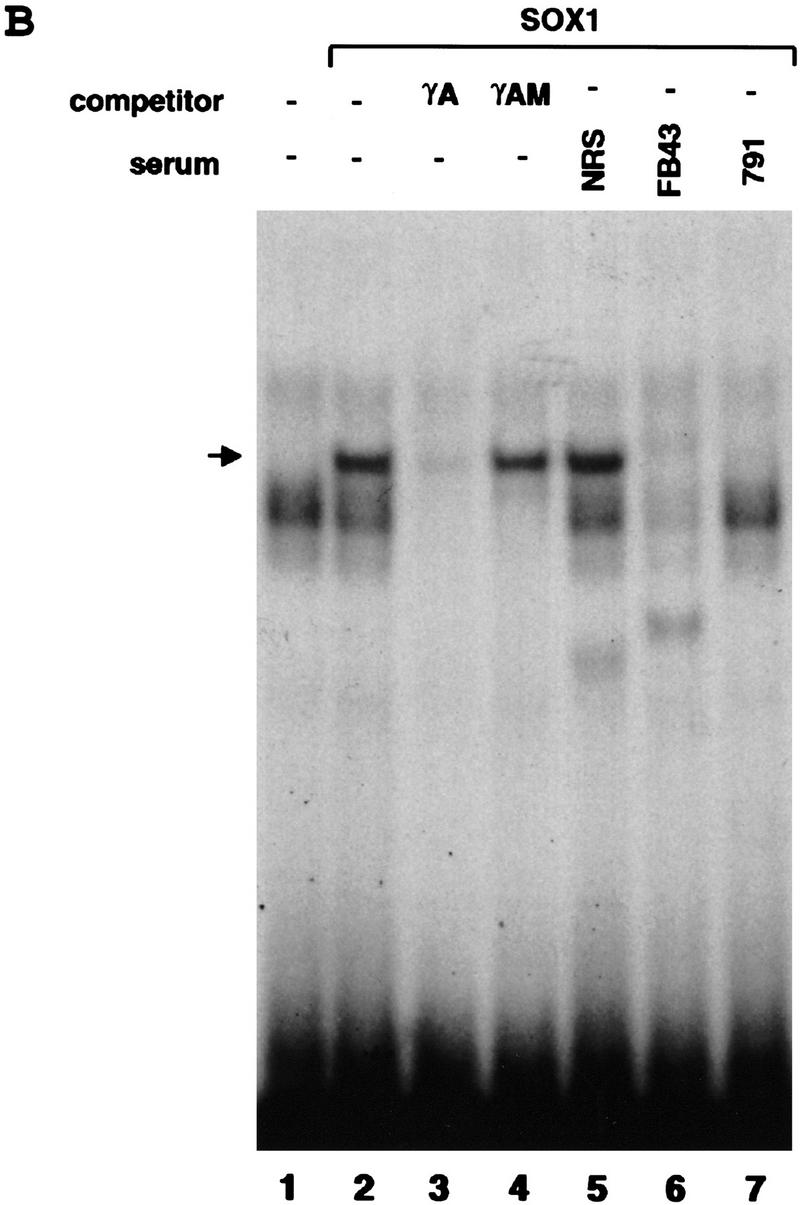
Binding of SOX1 protein to the mouse γA-crystallin promoter. (A) Complementary strand of SOX binding consensus sequence, wild-type (γA), and mutated (γAM) oligonucleotide sequence from the γA-crystallin promoter that was used for EMSA, promoter–sequence alignment of the six mouse γ-crystallin genes. Sequences identical to the consensus SOX binding site are shown in boldface type. The substituted nucleotides in γAM are underlined. Nucleotide positions of the γF-crystallin gene relative to the transcription start site are shown. (B) EMSA with recombinant SOX1 protein. γA oligonucleotide probe incubated without recombinant protein (in vitro transcription/translation reaction mixture incubated without DNA template) (lane 1) or with SOX1 recombinant protein (lanes 2–7). Assays were done in the presence of nonspecific competitor (lane 2), nonradioactive γA oligonucleotide (lane 3), nonradioactive mutated γAM oligonucleotide (lane 4), normal rabbit serum (NRS) (lane 5), SOX1 rabbit antiserum abFB43 (lane 6), or ab791 (lane 7) as shown. (→) The position of SOX1 complex.

