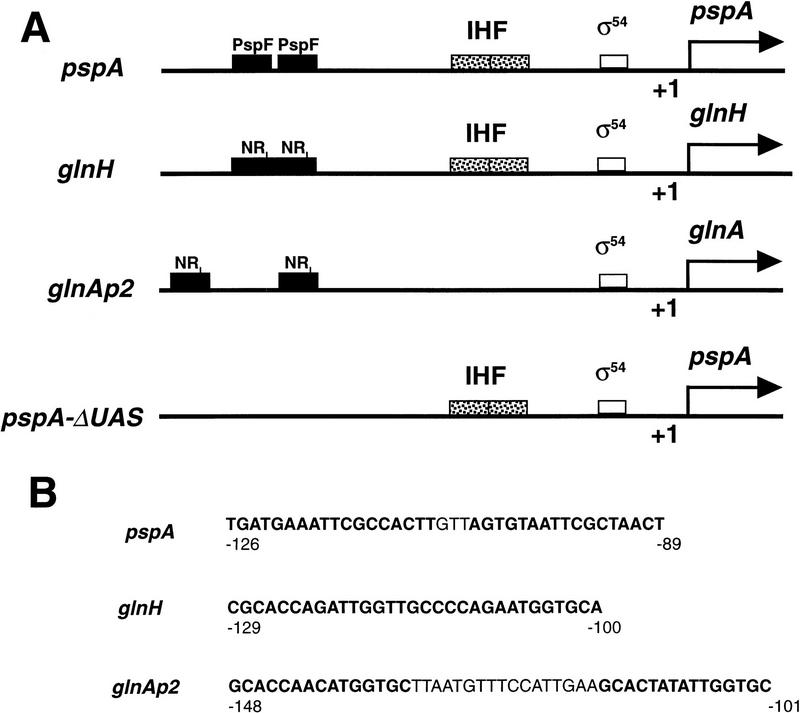
Figure 1.
Organization of σ54-dependent promoters and upstream activation sequences. (A) The pspA promoter contains an IHF-binding site (−30 to −65) (Weiner et al. 1995) and two high-affinity binding sites (−89 to −126) for the PspF transcriptional activator (Jovanovic 1997). The glnH promoter contains an IHF-binding site (−33 to −59), two overlapping high-affinity binding sites for the NRI transcriptional activator (−100 to −129), and two lower affinity NRI sites (not shown) (Claverie-Martin and Magasanik 1991). The glnAp2 promoter contains two high affinity NRI sites (−100 to −147) as well as three weaker NRI sites (not shown) (Reitzer and Magasanik 1986). The pspA–ΔUAS promoter is identical to the pspA promoter except that the sequences spanning the PspF binding sites were deleted (Dworkin et al. 1997). (B) The upstream activation sequences (in bold) of the promoters schematized in A. Note that the glnH UAS sequences are overlapping and that, whereas the glnH and glnAp2 UAS sequences are similar, they both differ from the pspA UAS sequences.