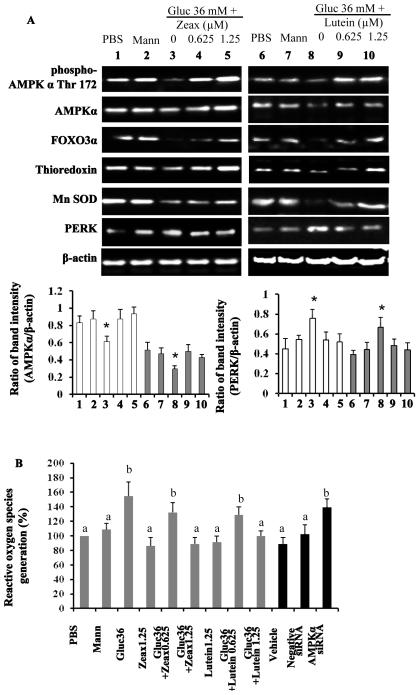
Figure 5. Zeaxanthin and/or lutein activation of AMPK protects human RPE cell culture against a high glucose challenge.
Human adult diploid RPE cell line ARPE-19 cells were treated with 36 mM glucose for 48 hours to mimic hyperglycemia condition in db/db mice. Zeaxanthin and/or lutein were simultaneously added into the culture medium. Mannitol was used as an osmotic control. The whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blot (A). β-actin was used as an euqal loading control to normalize each protein expression. Relative band intensity of each protein to β-actin was used for graphing and statistic analysis (* p<0.05, n=3, mean data on AMPK and PERK shown in lower graphs. Other mean data not shown). Zeaxanthin group samples #1 to #5: PBS, mannitol, glucose only, glucose with zeaxanthin 0.625 μM, and glucose with zeaxanthin 1.25 μM, * p<0.05 vs. the PBS (sample #1). Lutein group samples #6 to #10: PBS, mannitol, glucose only, glucose with lutein 0.625 μM, and glucose with lutein 1.25 μM, * p<0.05 vs. the PBS (sample #6).. The cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was determined (B). AMPKα was knocked down by its specific siRNA in the zeaxanthin (1.25 μM) treated ARPE-19 cells under a high glucose challenge. AMPKα siRNA knockdown-altered cellular ROS level was determined and expressed in the far right three black columns of graph B (p<0.05 vs the Vehicle). PBS, phosphate buffered saline; Mann, mannitol; Gluc, glucose; Zeax, zeaxanthin