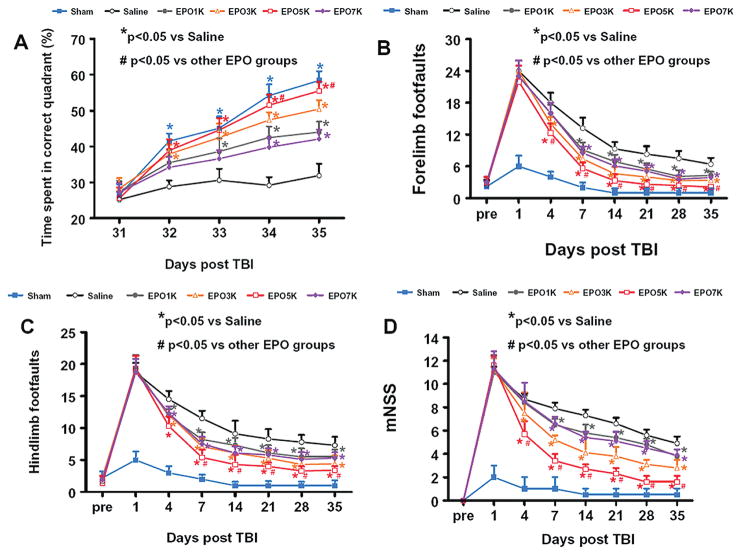
Fig. 2.
Effect of EPO treatment on functional outcomes. (A) Spatial learning measured by a recent version of the Morris water maze test at Days 31–35 after TBI. TBI significantly impaired spatial learning at Days 32–35 compared to sham controls (p < 0.05). Delayed treatment with EPO improves spatial learning performance at Days 33–35 compared with the saline group (p < 0.05). However, the spatial learning performance at Days 34 and 35 in the EPO5K group is better than that in other EPO groups (p < 0.05). (B) Effect of EPO on sensorimotor function (forelimb footfault) before and after TBI. Delayed EPO treatment significantly reduces forelimb foot faults at Days 7–35 while EPO3K and 5K treatment significantly reduces them at Day 4 compared with the saline group (p < 0.05). EPO5K shows better effects on reducing forelimb footfaults compared to other EPO groups at Days 4–35 (p < 0.05). (C) Effect of EPO on sensorimotor function (hindlimb footfault) before and after TBI. Delayed EPO treatment significantly reduces hindlimb foot faults at days 4–35 while EPO5K treatment significantly reduces them at Days 7 –35 compared with the other EPO groups (p < 0.05). (D) The plot shows the functional improvement detected on the modified neurological severity scores (mNSS). EPO treatment significantly lowers mNSS scores at Days 7–35 compared to saline group (p < 0.05). EPO3K and 5K significantly reduces mNSS scores at Day 4 (p < 0.05). However, the functional recovery (lowered mNSS score) at Days 4–35 in the EPO5K group is better than that in the EPO3K group (p < 0.05). Data represent mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 vs. Saline group. #p < 0.05 vs. other EPO groups. N (rats/group) =8.