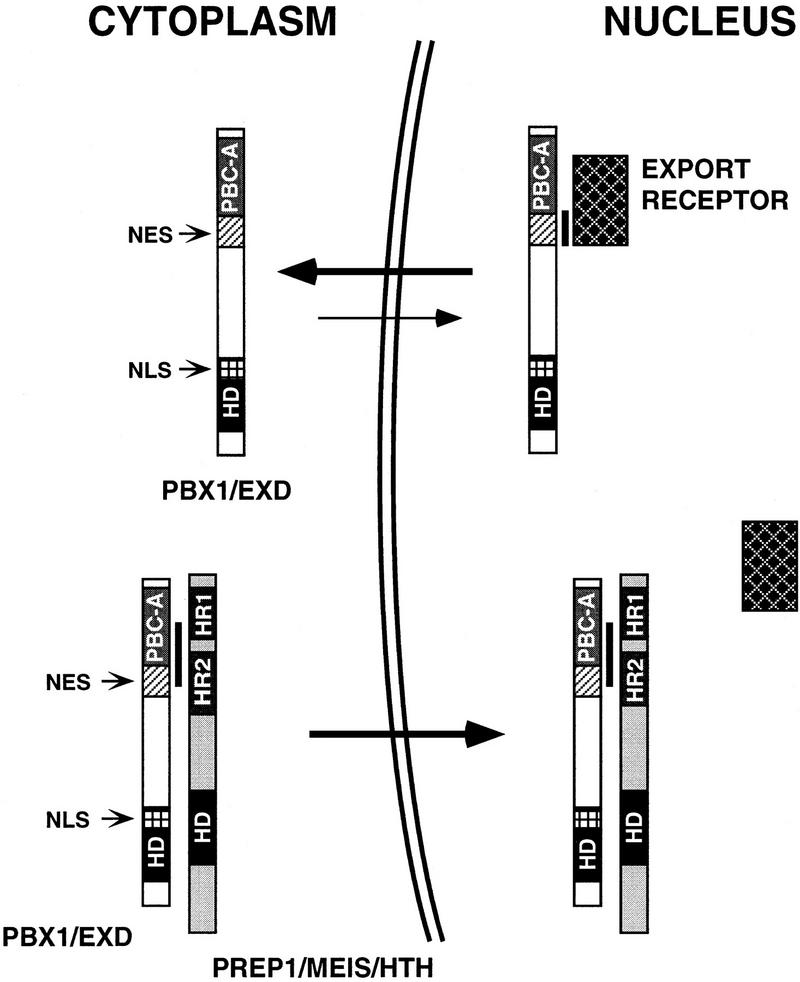
Figure 4.
A model for the regulation of subcellular localization of PBC and PREP1/MEIS/HTH proteins in cells displaying cytoplasmic localization of PBC proteins. PBC and PREP1/MEIS/HTH proteins are represented schematically. In specific cell contexts (e.g., Schneider cells), in the absence of PREP1/MEIS/HTH proteins, PBC proteins are actively exported from the nucleus, a process requiring sequences (NES, hatched box) located within their conserved PBC-A domain, which are recognized by a nuclear export receptor (dark, squared rectangle). PBC proteins form stable complexes with PREP1/MEIS/HTH proteins, when coexpressed, through an interaction surface that coincides with the region required for nuclear export, thereby shielding it. The newly formed complex translocates into the nucleus owing to the NLS located within the homeodomain of PBC proteins (NLS, white-squared box). Black rectangles represent the homeodomains (HD). Light gray and dark gray boxes represent conserved amino-terminal regions within PBC and PREP1/MEIS/HTH proteins, respectively (PBC-A, HR1/HR2). A black vertical line indicates protein–protein contacts.