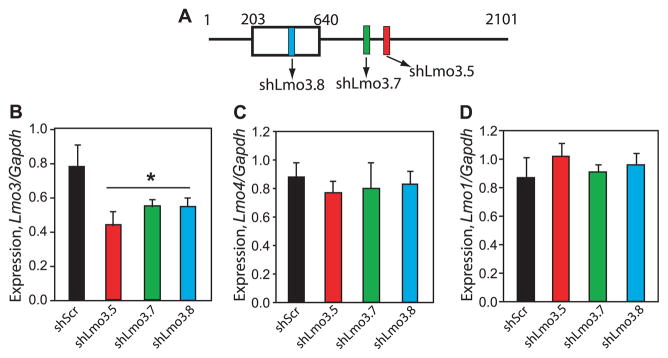
Fig. 2.
Efficacy of short-hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) targeting Lmo3 for RNA interference in Neuro-2a cells. (A) Schematic illustrating the position of shRNAs targeting the Lmo3 transcript. Colored boxes show shRNA location, open box illustrates the protein coding region, and numbers indicate the nucleotide position along the Lmo3 mRNA. (B) Expression of Lmo3 in Neuro-2a cells transfected with lentiviral plasmids expressing shRNAs targeting Lmo3 (shLmo3.5, shLmo3.7, and shLmo3.8) or the control shScr. RNA was isolated 2 days after transfection and subjected to qPCR. Lmo3 expression is normalized to expression of the housekeeping gene, Gapdh. Asterisk indicates a significant difference between the shLmo3 constructs and shScr by one-way ANOVA (*p = 0.007; n = 3). (C, D) Lmo4 (C) and Lmo1 (D) expression in transfected Neuro-2a samples described in (B).